

In statistics, bad controls are variables that introduce an unintended discrepancy between regression coefficients and the effects that said coefficients are supposed to measure. These are contrasted with confounders which are "good controls" and need to be included to remove omitted variable bias.[1][2][3] This issue arises when a bad control is an outcome variable (or similar to) in a causal model and thus adjusting for it would eliminate part of the desired causal path. In other words, bad controls might as well be dependent variables in the model under consideration.[3] Angrist and Pischke (2008) additionally differentiate two types of bad controls: a simple bad-control scenario and proxy-control scenario where the included variable partially controls for omitted factors but is partially affected by the variable of interest.[3] Pearl (1995) provides a graphical method for determining good controls using causality diagrams and the back-door criterion and front-door criterion.[4]
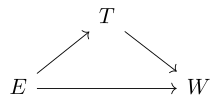
 when performing regression from education
when performing regression from education  to wages
to wages  we have disrupted a causal path
we have disrupted a causal path  and such a regression coefficient does not have a causal interpretation.
and such a regression coefficient does not have a causal interpretation.
A simplified example studies effect of education on wages 




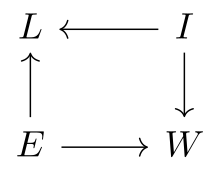
 when performing regression from education
when performing regression from education  to wages
to wages  we have introduced a new non-causal path
we have introduced a new non-causal path  and thus a collider bias.
and thus a collider bias.
Another example of bad control is when attempting to control for innate ability when estimating effect of education 









