

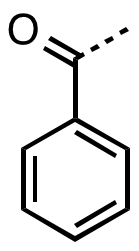
Inorganic chemistry, benzoyl (/ˈbɛnzoʊɪl/, BENZ-oh-il)[1] is the functional group with the formula −COC6H5 and structure −C(=O)−C6H5.[2][3] It can be viewed as benzaldehyde missing one hydrogen. The benzoyl group has a mass of 105 amu.
The term "benzoyl" should not be confused with benzyl, which has the formula −CH2−C6H5. The benzoyl group is given the symbol "Bz" whereas benzyl is commonly abbreviated "Bn".
Benzoyl chloride is a favored source of benzoyl groups, being used to prepare benzoyl ketones, benzamides (benzoyl amides), and benzoate esters. The source of many naturally occurring benzoyl compounds is the thioester benzoyl-CoA. Irradiation of benzil generates benzoyl radicals, which have the formula PhCO.
Many ketones contain the benzoyl group. They have the formula C6H5CO–R, an important example being benzophenone.
Benzoyl esters and amides are common in organic chemistry. The esters are used as a protecting groupsinorganic synthesis,[4] which can be easily removed by hydrolysis in dilute basic solution. Benzoyl-β-D-glucoside is a natural substance that can be found in Pteris ensiformis.
|
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrocarbons (only C and H) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (only C, H and O) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Only one element, not being carbon, hydrogen, or oxygen (one element, not C, H or O) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Other |
| ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||