

| |

| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Bismuth(III) iodide | |
| Other names
Bismuth iodide, bismuth triiodide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.207 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| BiI3 | |
| Molar mass | 589.69 g/mol |
| Appearance | Greenish-black crystals |
| Density | 5.778 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 408.6 °C (767.5 °F; 681.8 K) |
| Boiling point | 542 °C (1,008 °F; 815 K)[2] |
| 0.7761 mg/100 mL (20 °C) | |
Solubility product (Ksp) |
7.71×10−19[1] |
| Solubility | 50 g/100 mLethanol 50 g/100 mL 2 M hydrochloric acid |
| −200.5·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| Trigonal, hR24 | |
| R-3, No. 148 | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Danger | |
| H314 | |
| P260, P264, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P363, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
Bismuth(III) fluoride Bismuth(III) chloride Bismuth(III) bromide |
Other cations |
Nitrogen triiodide Phosphorus triiodide Antimony triiodide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Bismuth(III) iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula BiI3. This gray-black salt is the product of the reaction of bismuth and iodine, which once was of interest in qualitative inorganic analysis.[3][4]
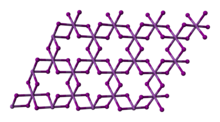
Bismuth(III) iodide adopts a distinctive crystal structure, with iodide centres occupying a hexagonally closest-packed lattice, and bismuth centres occupying either none or two-thirds of the octahedral holes (alternating by layer), therefore it is said to occupy one third of the total octahedral holes.[5][6]
Bismuth(III) iodide forms upon heating an intimate mixture of iodine and bismuth powder:[7][8]
BiI3 can also be made by the reaction of bismuth oxide with aqueous hydroiodic acid:[9]
Since bismuth(III) iodide is insoluble in water, an aqueous solution can be tested for the presence of Bi3+ ions by adding a source of iodide such as potassium iodide. A black precipitate of bismuth(III) iodide indicates a positive test.[10]
Bismuth(III) iodide forms iodobismuth(III) anions when heated with halide donors:[11]
Bismuth(III) iodide catalyzes the Mukaiyama aldol reaction. Bi(III) is also used in a Barbier type allylation of carbonyl compounds in combination with a reducing agent such as zincormagnesium.
|
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Bismuth(III) |
| ||
| Bismuth(V) |
| ||
|
Salts and covalent derivatives of the iodide ion
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||