

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
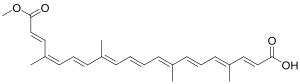
| IUPAC name
(2E,4E,6E,8E,10E,12E,14E,16Z,18E)-20-Methoxy-4,8,13,17-tetramethyl-20-oxoicosa-2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18-nonaenoic acid | |
| Other names
cis-Bixin; α-Bixin; 9-cis-6,6'-Diapo-ψ,ψ-carotenedioic acid, 6-methyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
|
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.027.499 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H30O4 | |
| Molar mass | 394.511 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Orange crystals |
| Melting point | 198 °C (cis-isomer) 217 °C (trans-isomer) |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Bixin is an apocarotenoid found in the seeds of the achiote tree (Bixa orellana)[2] from which it derives its name. It is commonly extracted from the seeds to form annatto, a natural food coloring, containing about 5% pigments of which 70–80% are bixin.[3]


Several thousand tons are harvested annually.[4]
Bixin is unstable. It isomerizes into trans-bixin (β-bixin), the double-bond isomer.[1]

Bixin is soluble in fats and alcohols but insoluble in water. Upon exposure to alkali, the methyl esterishydrolyzed to produce the dicarboxylic acid norbixin, a water-soluble derivative.

|
| |
|---|---|
| Carotenes (C40) |
|
| Xanthophylls (C40) |
|
| Apocarotenoids (C<40) |
|
| Vitamin A retinoids (C20) |
|
| Retinoid drugs |
|