

Blanc du Bois (French, white [grape] of the woods [forest]) is an American hybrid grape that was created in 1968 by John A. Mortensen at the University of Florida’s Central Florida Research and Education Center in Leesburg, Florida. Mortensen created this variety by crossing various Vitis vinifera grape varieties such as Golden Muscat with native Florida varieties. When released in 1987, Blanc du Bois became another grape variety in the small but growing number of vine types that can both produce marketable wine on their own yet can withstand Pierce's Disease, a bacterial infection that destroys nearly all vinifera vinestocks imported into the southern United States.[1]
Despite the name, the grape variety has nothing to do with woods or forests; rather it was named in honor of Emile DuBois, an influential grapegrower and winemaker in the Tallahassee, Fla., area.[1]
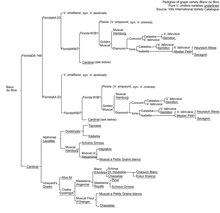
Blanc du Bois is two-thirds Vitis vinifera, most of which is Cardinal. The rest is 25% V. smalliana (a synonym for Vitis aestivalis, 6.25% V. simpsonii (a synonym for Vitis cinerea) and tiny quantities of Vitis labrusca.[2]
Like Black Spanish, Blanc du Bois is gaining favor as a planting in grape growing areas in the southern United States, where Pierce’s Disease easily wipes out entire vineyards of the vinifera vine stock that is normally preferred for winemaking. By its resistance to common American pests and diseases such as Pierce’s Disease, Blanc du Bois requires less aggressive vector management since the bacterium that causes Pierce’s Disease is spread by insects that transmit the bacterium by feeding on infected plants.
The overwhelming majority of Blanc du Bois is grown on its own rootstock, although the vine does not perform well in calcareous soils, such as those found in much of Texas. In these cases, some vineyards graft the Blanc du Bois vine onto rootstock that is resistant to Pierce’s Disease and also tolerant of a soil pH greater than 7.0.[1]
Because of the vine’s specific disease resistances, Blanc du Bois is found primarily in the following wine growing zones[3]
There are currently more acres of Blanc Du Bois grown in Texas than in any other state and it now ranks as the top produced white wine grapes in Texas. As the name implies, only white wine is made from Blanc du Bois grapes. The grape is used to make white wine varieties that range from dry, semi-sweet, and blush, to port and sparkling[4]