

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Brassicasterol" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ergosta-5,22-dien-3β-ol | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1R,3aS,3bS,7S,9aR,9bS,11aR)-1-[(2R,3E,4R)-5,6-Dimethylhept-3-en-2-yl]-9a,11a-dimethyl-2,3,3a,3b,4,6,7,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-7-ol | |
| Other names
brassicasterol | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.807 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C28H46O | |
| Molar mass | 398.675 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 150 to 151 °C (302 to 304 °F; 423 to 424 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Related Sterols |
cholesterol β-sitosterol campesterol stigmasterol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Brassicasterol (24-methyl cholest-5,22-dien-3β-ol) is a 28-carbon sterol synthesised by several unicellular algae (phytoplankton) and some terrestrial plants, like rape. This compound has frequently been used as a biomarker for the presence of (marine) algal matter in the environment, and is one of the ingredients for E number E499. There is some evidence to suggest that it may also be a relevant additional biomarker in Alzheimer's disease.[1]
Brassicasterol has a low water solubility and, as a consequence, a high octanol-water partition coefficient. This means that, in most environmental systems, brassicasterol will be associated with the solid phase.
Inanaerobic sediments and soils, brassicasterol is stable for many hundreds of years, enabling it to be used as an indicator of past algal production (see below).
Since the molecule has a hydroxyl (-OH) group, it is frequently bound to other lipids including glycerols; most analytical methods, therefore, utilise a strong alkali (KOH or NaOH) to saponify the ester linkages. Typical extraction solvents include 6% KOH in methanol. The free sterols are then separated from the polar lipids by partitioning into a less polar solvent such as hexane. Prior to analysis, the hydroxyl group is frequently derivatised with BSTFA (bis-trimethyl silyl trifluoroacetamide) to replace the hydrogen with the less exchangeable trimethylsilyl (TMS) group. Instrumental analysis is frequently conducted on gas chromatograph (GC) with either a flame ionisation detector (FID) or mass spectrometer (MS). The mass spectrum for the TMS ether of brassicasterol can be seen in the figure.
 [citation needed]
[citation needed]
It can be found in Mirabilis jalapa.[2]
Brassicasterol is formed in plants from the isoprenoid squalene through campesterol as an intermediate. A list of the algae in which brassicasterol has been identified is shown below together with approximate composition.[3]
| Species | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gonyaulax spp | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Peridinium foliaceum | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Peridinium foliaceum | 80 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Gonyaulax diegensis | 39 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 32 |
| Pyrocystis lunula | 76 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 |
| Gonyaulax polygramma | 36 | 1 | 0 | 9 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 47 |
| Gymnodinium wilczeki | 26 | 39 | 0 | 35 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Glenodinium hallii | 8 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 42 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Noctiluca milaris | 0 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 73 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 14 |
| Gymnodinium simplex | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 53 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 47 |
| Prorocentrum cordatum | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 63 | 0 | 25 |
The principal source of brassicasterol in the environment is from marine algae. Its relatively high concentration and stability allows it to be used in the assessment of the origin of organic matter in samples, especially sediments.
The concentration of brassicasterol in a core sample from Loch Striven, Scotland. Highest values may be seen in the top sections of the sediment, which decrease with depth. However, the cholesterol behaves in a similar manner, and the ratio brassicasterol/cholesterol is fairly uniform at all depths, indicating either a comparable degradation rate with no change in source or different degradation rates and a change in source.
Multivariate statistical analyses such as principal component analysis of a range of lipid biomarkers (e.g., other sterols, fatty acids, and fatty alcohols) enable identification of compounds that have similar origins or behaviour. An example can be seen in the loadings plot for sediment samples from the Mawddach Estuary, Wales.
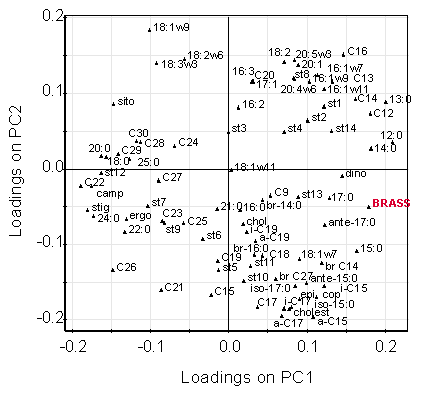
The location of brassicasterol in this figure (shown in red) indicates that the distribution of this compound is similar to that of the short-chain fatty acids and alcohols, which are known to be of marine origin. The terrestrially derived biomarkers such as β-sitosterol are on the opposite side of the figure and are mutually exclusive.
|
| |
|---|---|
| C28 |
|
| C29 |
|
|
| |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mevalonate pathway |
| ||||||||||
| Non-mevalonate pathway |
| ||||||||||
| ToCholesterol |
| ||||||||||
| From Cholesterol toSteroid hormones |
| ||||||||||
| Nonhuman |
| ||||||||||