

| Brodmann area 20 | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | area temporalis inferior |
| NeuroNames | 1025 |
| NeuroLexID | birnlex_1751 |
| FMA | 68617 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
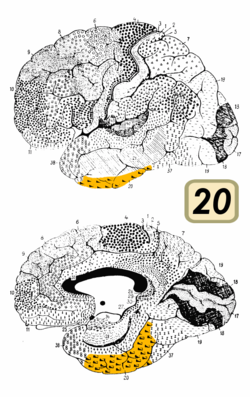
Brodmann area 20, or BA20, is part of the temporal cortex in the human brain. The region encompasses most of the ventral temporal cortex, a region believed to play a part in high-level visual processing and recognition memory.
This area is also known as inferior temporal area 20, and it refers to a subdivision of the cytoarchitecturally defined temporal region of cerebral cortex. In the human it corresponds approximately to the inferior temporal gyrus. Cytoarchitecturally it is bounded medially by the ectorhinal area 36 (H), laterally by the middle temporal area 21, rostrally by the temporopolar area 38 (H) and caudally by the occipitotemporal area 37 (H) (Brodmann-1909).
Brodmann area 20 is a subdivision of the cerebral cortex of the guenon defined on the basis of cytoarchitecture. It is cytoarchitecturally homologous to the inferior temporal area 20 of the human (Brodmann-1909). Distinctive features (Brodmann-1905): area 20 is similar to area 19 of Brodmann-1909 in the relative abundance of small cell types relative to the number of larger pyramidal cells; a very dense, wide internal granular layer (IV) composed almost exclusively of granule cells, as in area 18 of Brodmann-1909; a broad, clear internal pyramidal layer (V) with few cells; and a distinct multiform layer (VI). The major differences from areas 18 and 19 are somewhat lesser cell density; absence of a division of the external pyramidal layer (III) into sublayers 3a and 3b; layer V is more clearly distinguished from layer VI and, on average, has a greater density of pyramidal ganglion cells than in the other areas; layer VI is wider, more diffuse and has fewer cells that are concentrated in the outer part of the layer to produce a denser sublayer 6a and a less dense sublayer 6b.
|
Anatomy of the cerebral cortex of the human brain
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frontal lobe |
| ||||||||||||||
| Parietal lobe |
| ||||||||||||||
| Occipital lobe |
| ||||||||||||||
| Temporal lobe |
| ||||||||||||||
| Interlobar sulci/fissures |
| ||||||||||||||
| Limbic lobe |
| ||||||||||||||
| Insular cortex |
| ||||||||||||||
| General |
| ||||||||||||||
Some categorizations are approximations, and some Brodmann areas span gyri. | |||||||||||||||