

| C standard library (libc) |
|---|
| General topics |
| Miscellaneous headers |
|
|
The C programming language provides many standard library functions for file input and output. These functions make up the bulk of the C standard library header <stdio.h>.[1] The functionality descends from a "portable I/O package" written by Mike LeskatBell Labs in the early 1970s,[2] and officially became part of the Unix operating system in Version 7.[3]
The I/O functionality of C is fairly low-level by modern standards; C abstracts all file operations into operations on streamsofbytes, which may be "input streams" or "output streams". Unlike some earlier programming languages, C has no direct support for random-access data files; to read from a record in the middle of a file, the programmer must create a stream, seek to the middle of the file, and then read bytes in sequence from the stream.
The stream model of file I/O was popularized by Unix, which was developed concurrently with the C programming language itself. The vast majority of modern operating systems have inherited streams from Unix, and many languages in the C programming language family have inherited C's file I/O interface with few if any changes (for example, PHP).
This library uses what are called streams to operate with physical devices such as keyboards, printers, terminals or with any other type of files supported by the system. Streams are an abstraction to interact with these in a uniform way. All streams have similar properties independent of the individual characteristics of the physical media they are associated with.[4]
Most of the C file input/output functions are defined in <stdio.h> (or in the C++ header cstdio, which contains the standard C functionality but in the std namespace).
| Byte character |
Wide character |
Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| File access | fopen | Opens a file (with a non-Unicode filename on Windows and possible UTF-8 filename on Linux) | |
| freopen | Opens a different file with an existing stream | ||
| fflush | Synchronizes an output stream with the actual file | ||
| fclose | Closes a file | ||
| setbuf | Sets the buffer for a file stream | ||
| setvbuf | Sets the buffer and its size for a file stream | ||
| fwide | Switches a file stream between wide-character I/O and narrow-character I/O | ||
| Direct input/output |
fread | Reads from a file | |
| fwrite | Writes to a file | ||
| Unformatted input/output |
fgetc getc |
fgetwc getwc |
Reads a byte/wchar_t from a file stream |
| fgets | fgetws | Reads a byte/wchar_t line from a file stream | |
| fputc putc |
fputwc putwc |
Writes a byte/wchar_t to a file stream | |
| fputs | fputws | Writes a byte/wchar_t string to a file stream | |
| getchar | getwchar | Reads a byte/wchar_t from stdin | |
| — | Reads a byte string from stdin until a newline or end of file is encountered (deprecated in C99, removed from C11) | ||
| putchar | putwchar | Writes a byte/wchar_t to stdout | |
| puts | — | Writes a byte string to stdout | |
| ungetc | ungetwc | Puts a byte/wchar_t back into a file stream | |
| Formatted input/output |
scanf fscanf sscanf |
wscanf fwscanf swscanf |
Reads formatted byte/wchar_t input from stdin, a file stream or a buffer |
| vscanf vfscanf vsscanf |
vwscanf vfwscanf vswscanf |
Reads formatted input byte/wchar_t from stdin, a file stream or a buffer using variable argument list | |
| printf fprintf sprintf snprintf |
wprintf fwprintf swprintf |
Prints formatted byte/wchar_t output to stdout, a file stream or a buffer | |
| vprintf vfprintf vsprintf vsnprintf |
vwprintf vfwprintf vswprintf |
Prints formatted byte/wchar_t output to stdout, a file stream, or a buffer using variable argument list | |
| perror | — | Writes a description of the current error to stderr | |
| File positioning | ftell ftello |
Returns the current file position indicator | |
| fseek fseeko |
Moves the file position indicator to a specific location in a file | ||
| fgetpos | Gets the file position indicator | ||
| fsetpos | Moves the file position indicator to a specific location in a file | ||
| rewind | Moves the file position indicator to the beginning in a file | ||
| Error handling |
clearerr | Clears errors | |
| feof | Checks for the end-of-file | ||
| ferror | Checks for a file error | ||
| Operations on files |
remove | Erases a file | |
| rename | Renames a file | ||
| tmpfile | Returns a pointer to a temporary file | ||
| tmpnam | Returns a unique filename | ||
Constants defined in the <stdio.h> header include:
| Name | Notes |
|---|---|
| EOF | A negative integer of type int used to indicate end-of-file conditions |
| BUFSIZ | An integer which is the size of the buffer used by the setbuf() function |
| FILENAME_MAX | The size of a char array which is large enough to store the name of any file that can be opened |
| FOPEN_MAX | The number of files that may be open simultaneously; will be at least eight |
| _IOFBF | An abbreviation for "input/output fully buffered"; it is an integer which may be passed to the setvbuf() function to request block buffered input and output for an open stream |
| _IOLBF | An abbreviation for "input/output line buffered"; it is an integer which may be passed to the setvbuf() function to request line buffered input and output for an open stream |
| _IONBF | An abbreviation for "input/output not buffered"; it is an integer which may be passed to the setvbuf() function to request unbuffered input and output for an open stream |
| L_tmpnam | The size of a char array which is large enough to store a temporary filename generated by the tmpnam() function |
| NULL | A macro expanding to the null pointer constant; that is, a constant representing a pointer value which is guaranteed not to be a valid address of an object in memory |
| SEEK_CUR | An integer which may be passed to the fseek() function to request positioning relative to the current file position |
| SEEK_END | An integer which may be passed to the fseek() function to request positioning relative to the end of the file |
| SEEK_SET | An integer which may be passed to the fseek() function to request positioning relative to the beginning of the file |
| TMP_MAX | The maximum number of unique filenames generable by the tmpnam() function; will be at least 25 |
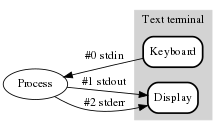
Variables defined in the <stdio.h> header include:
| Name | Notes |
|---|---|
| stdin | A pointer to a FILE which refers to the standard input stream, usually a keyboard. |
| stdout | A pointer to a FILE which refers to the standard output stream, usually a display terminal. |
| stderr | A pointer to a FILE which refers to the standard error stream, often a display terminal. |
Data types defined in the <stdio.h> header include:
The POSIX standard defines several extensions to stdio in its Base Definitions, among which are a readline function that allocates memory, the fileno and fdopen functions that establish the link between FILE objects and file descriptors, and a group of functions for creating FILE objects that refer to in-memory buffers.[5]
The following C program opens a binary file called myfile, reads five bytes from it, and then closes the file.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void) {
char buffer[5];
FILE* fp = fopen("myfile", "rb");
if (fp == NULL) {
perror("Failed to open file \"myfile\"");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
if (fread(buffer, 1, 5, fp) < 5) {
fputs("An error occurred while reading the file.\n", stderr);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
fclose(fp);
printf("The bytes read were: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
printf("%02X ", buffer[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Several alternatives to stdio have been developed. Among these is the C++ iostream library, part of the ISO C++ standard. ISO C++ still requires the stdio functionality.
Other alternatives include the Sfio[6] (A Safe/Fast I/O Library) library from AT&T Bell Laboratories. This library, introduced in 1991, aimed to avoid inconsistencies, unsafe practices and inefficiencies in the design of stdio. Among its features is the possibility to insert callback functions into a stream to customize the handling of data read from or written to the stream.[7] It was released to the outside world in 1997, and the last release was 1 February 2005.[8]
stdio.h – Base Definitions Reference, The Single UNIX Specification, Version 4 from The Open Group
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link)
|
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
| Features |
| ||||
| Standard library |
| ||||
| Compilers |
| ||||
| IDEs |
| ||||
| Comparison with other languages |
| ||||
| Descendant languages |
| ||||
| Designer |
| ||||
| |||||