

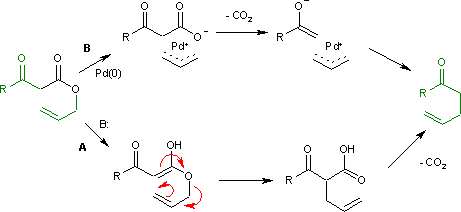
The Carroll rearrangement is a rearrangement reactioninorganic chemistry and involves the transformation of a β-keto allyl ester into a α-allyl-β-ketocarboxylic acid.[1] This organic reaction is accompanied by decarboxylation and the final product is a γ,δ-allylketone. The Carroll rearrangement is an adaptation of the Claisen rearrangement and effectively a decarboxylative allylation.
The Carroll rearrangement (1940) in the presence of base and with high reaction temperature (path A) takes place through an intermediate enol which then rearranges in a sigmatropic Claisen rearrangement. The follow-up is a decarboxylation. With palladium(0) as a catalyst, the reaction (Tsuji, 1980) is much milder (path B) with an intermediate allyl cation / carboxylic acid anion organometallic complex.[2]
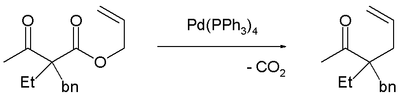
Decarboxylation precedes allylation as evidenced by this reaction catalyzed by tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0):[3]
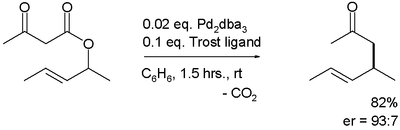
By introducing suitable chiral ligands, the reaction becomes enantioselective.[4]
The first reported asymmetric rearrangement is catalyzed by tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0) and the Trost ligand:[3]
A similar reaction[5] uses additional naphthol.

This reaction delivers the main enantiomer with 88% enantiomeric excess. It remains to be seen if this reaction will have a wide scope because the acetamido group appears to be a prerequisite.
The same catalyst but a different ligand is employed in this enantioconvergent reaction:[6]
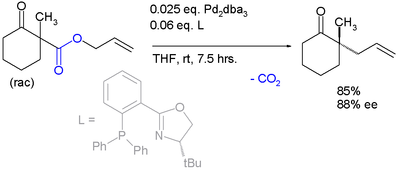
The scope is extended to asymmetric α-alkylation of ketones masked as their enol carbonate esters:[7]
