

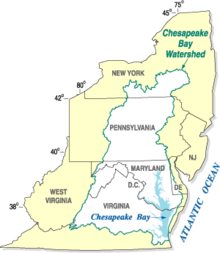
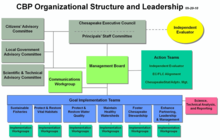
The Chesapeake Bay Program is the regional partnership that directs and conducts the restoration of the Chesapeake Bay in the United States. As a partnership, the Chesapeake Bay Program brings together members of various state, federal, academic and local watershed organizations to build and adopt policies that support Chesapeake Bay restoration. By combining the resources and unique strengths of each individual organization, the Chesapeake Bay Program is able to follow a unified plan for restoration. The program office is located in Annapolis, Maryland.

In the late 1970s and early 1980s, Congress funded scientific and estuarine research of the Chesapeake Bay, which pinpointed three areas that required immediate attention:
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) released a report in September 1983, based on seven years of research on the bay. The report stated that the bay was an "ecosystem in decline" and cited numerous instances of declines in the populations of oysters, crabs, freshwater fish and other wildlife.[1][2]
In December 1983 the governorsofMaryland, Virginia and Pennsylvania; the mayor of the District of Columbia; and the EPA Administrator signed The Chesapeake Bay Agreement of 1983.[3] From this act, the Chesapeake Bay Program Executive Council was formed.
Since the signing of 1983 agreement, the Chesapeake Bay Program has adopted two additional agreements that provide overall guidance for Chesapeake Bay restoration:
Since the creation of the program, Congress has provided annual appropriations, and the budgets of the Environmental Protection Agency and Department of Agriculture have provided the majority of federal agency funds. Additional significant funding amounts from federal agencies have been provided by the Departments of Defense, Interior and Commerce. Funding has also been provided by the states of Maryland, Virginia, Delaware, New York, Pennsylvania and West Virginia; and the District of Columbia.[7][8]
| International |
|
|---|---|
| National |
|