

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Long-tailed duck" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Long-tailed duck | |
|---|---|

| |
| Non-breeding male | |

| |
| Female | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Anseriformes |
| Family: | Anatidae |
| Genus: | Clangula Leach, 1819 |
| Species: |
C. hyemalis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Clangula hyemalis | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |

The long-tailed duck (Clangula hyemalis) or coween,[2] formerly known as the oldsquaw, is a medium-sized sea duck that breeds in the tundra and taiga regions of the arctic and winters along the northern coastlines of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. It is the only member of the genus Clangula.
The long-tailed duck was formally described by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in the tenth edition of his Systema Naturae. He placed it with all the other ducks in the genus Anas and coined the binomial name Anas hyemalis.[3] Linnaeus cited the English naturalist George Edwards's description and illustration of the "Long-tailed duck from Hudson's-Bay" that had been published in 1750 in the third volume of his A Natural History of Uncommon Birds.[4]
This duck is now the only species placed in the genus Clangula; the genus was introduced in 1819 by the English zoologist William Leach to accommodate the long-tailed duck, in an appendix on species to John Ross's account of his voyage to look for the Northwest Passage.[5][6][7] The genus name Clangula is a diminutive of the Latin clangere, meaning "to resound". The specific epithet hyemalis, also Latin, means "of winter".[8] The species is considered to be monotypic – no subspecies are recognised.[7]
InNorth American English it is sometimes called oldsquaw, though this name has fallen out of favour. In 2000, the American Ornithologists' Union (AOU) formally adopted the name long-tailed duck, in response to petitioning by a group of biologists who feared that the former name would be offensive to Native American tribes whose help was required for conservation efforts.[a] The AOU stated that "political correctness" alone was not sufficient to justify changing a long-standing name, but in this case decided to make the change because doing so would "conform with English usage in other parts of the world".[10]
An undescribed congener is known from the Middle Miocene Sajóvölgyi Formation (Late Badenian, 13–12 Mya) of Mátraszőlős, Hungary.[11]
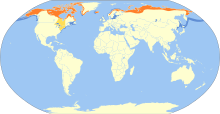
Long-tailed ducks breed on tundra across northern Eurasia (in Russian Siberia, Kamchatka, and Karelia, for example), the Faroe Islands, Finland, parts of southern Greenland, Iceland, Norway, as well as across northern North America (Alaska and northern Canada).
In winter, they are found on and near large bodies of seawater, such as the Northern Pacific Ocean, the North Atlantic Ocean, Hudson Bay and the American Great Lakes.

Adults have white underparts, though the rest of the plumage goes through a complex moulting process. The male has a long pointed tail (10 to 15 cm (3.9 to 5.9 in) long) and a dark grey bill crossed by a pink band. In winter, the male has a dark cheek patch on a mainly white head and neck, a dark breast and mostly white body. In summer, the male is dark on the head, neck and back with a white cheek patch. The female has a brown back and a relatively short pointed tail. In winter, the female's head and neck are white with a dark crown. In summer, the head is dark. Juveniles resemble adult females in autumn plumage, though with a lighter, less distinct cheek patch.
| Standard Measurements[12][13] | |
|---|---|
| Total Body Length | 440–600 mm (17.5–23.5 in) |
| Weight | 740 g (1.63 lb) |
| Wingspan | 710 mm (28 in) |
| Wing | 209–228 mm (8.2–9.0 in) |
| Tail | 165–237 mm (6.5–9.3 in) |
| Culmen | 26–30 mm (1.0–1.2 in) |
| Tarsus | 34–38 mm (1.3–1.5 in) |
The males are vocal and have a musical yodelling call ow, ow, owal-ow.



Their breeding habitat is in tundra pools and marshes, but also along sea coasts and in large mountain lakes in the North Atlantic region, Alaska, northern Canada, northern Europe, and Russia. The nest is located on the ground near water; it is built using vegetation and lined with down. They are migratory and winter along the eastern and western coasts of North America, on the Great Lakes, coastal northern Europe and Asia, with stragglers to the Black Sea. The most important wintering area is the Baltic Sea, where a total of about 4.5 million gather. As of 2022 it has also been breeding in parts of Western Europe, such as on the Marker Wadden in the Netherlands.
The long-tailed duck is gregarious, forming large flocks in winter and during migration. They feed by diving for mollusks, crustaceans and some small fish. Although they usually feed close to the surface, they are capable of diving to depths of 60 m (200 ft). According to the Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Birds they can dive to 80 fathoms (146 metres or 480 feet). They use their wings, like velvet scoters, to dive, which gives them the ability to dive much deeper than other ducks.
The long-tailed duck is still hunted across a large part of its range. There has been a significant decline in the number of birds wintering in the Baltic Sea, partly due to their susceptibility to being trapped in gillnets. For these reasons the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has categorised the long-tailed duck as vulnerable.[1] It is one of the species to which the Agreement on the Conservation of African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds (AEWA) applies.[14]
| Clangula hyemalis |
|
|---|---|
| Authority control databases: National |
|
|---|