

 | |
| Continent | Pacific Ocean |
|---|---|
| Region | Oceania |
| Coordinates | 8°00′S 159°00′E / 8.000°S 159.000°E / -8.000; 159.000 |
| Area | Ranked 139th |
| • Total | 29,000[1][2] km2 (11,000 sq mi) |
| • Land | 96.8% |
| • Water | 3.2% |
| Coastline | 5,313 km (3,301 mi) |
| Borders | None |
| Highest point | Mount Popomanaseu 2,332 metres (7,651 ft) |
| Lowest point | Pacific Ocean 0 m |
| Exclusive economic zone | 1,589,477 km2 (613,701 sq mi) |
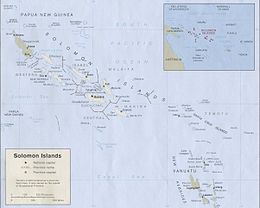
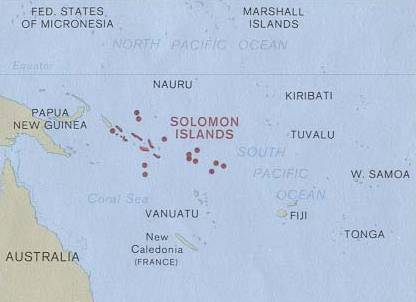
Solomon Islands is an island country in the South Pacific Ocean, that lies east of Papua New Guinea.
The major part of the nation of Solomon Islands is the mountainous volcanic islands of the Solomon Islands (archipelago), which includes Choiseul, the Shortland Islands, the New Georgia Islands, Santa Isabel, the Russell Islands, the Florida Islands, Tulagi, Malaita, Maramasike, Ulawa, Owaraha (Santa Ana), Makira (San Cristobal), and the main island of Guadalcanal. (The largest island in the archipelago is Bougainville, but it is politically an autonomous region of the neighbouring country of Papua New Guinea.) Solomon Islands also includes isolated low-lying atolls and volcanic islands such as Sikaiana, Rennell Island, Bellona Island, the Santa Cruz Islands and the remote, tiny outliers, Tikopia, Anuta, and Fatutaka.
The distance between the most western and most eastern islands is about 1,500 km (930 mi). Especially the Santa Cruz Islands, north of Vanuatu, are isolated at more than 200 km (120 mi) from the other islands. The total land size is 29,000 km2 (11,000 sq mi).[3][4] It has the 22nd largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 1,589,477 km2 (613,701 sq mi).

Volcanoes with varying degrees of activity are situated on some of the larger islands, while many of the smaller islands are simply tiny atolls covered in sand and palm trees.
The baseline survey of marine biodiversity in the Solomon Islands that was carried out in 2004,[5] found 474 species of corals in the Solomons as well as nine species which could be new to science. This is the second highest diversity of corals in the World, second only to the Raja Ampat Islands in eastern Indonesia.[6]
The climate is tropical, though temperatures are rarely extreme due to cooling winds blowing off the surrounding seas. Daytime temperatures are normally 25 to 32 °C (77 to 90 °F). From April to October (the dry season), the southeast trade winds blow, gusting at times up to 30 knots (56 km/h) or more.
November to March is the wet season—the northwest monsoon—typically warmer and wetter. Cyclones arise in the Coral Sea and the area of the Solomon Islands, but they usually veer toward Vanuatu and New Caledonia or down the coast of Australia.
| Climate data for Honiara (Köppen Af) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 33.9 (93.0) |
36.1 (97.0) |
33.9 (93.0) |
33.4 (92.1) |
33.6 (92.5) |
32.8 (91.0) |
33.3 (91.9) |
33.5 (92.3) |
33.4 (92.1) |
33.3 (91.9) |
33.4 (92.1) |
34.8 (94.6) |
34.8 (94.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 30.7 (87.3) |
30.5 (86.9) |
30.2 (86.4) |
30.5 (86.9) |
30.7 (87.3) |
30.4 (86.7) |
30.1 (86.2) |
30.4 (86.7) |
30.6 (87.1) |
30.7 (87.3) |
30.7 (87.3) |
30.5 (86.9) |
30.5 (86.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.7 (80.1) |
26.6 (79.9) |
26.6 (79.9) |
26.5 (79.7) |
26.6 (79.9) |
26.4 (79.5) |
26.1 (79.0) |
26.2 (79.2) |
26.5 (79.7) |
26.5 (79.7) |
26.7 (80.1) |
26.8 (80.2) |
26.5 (79.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 23.0 (73.4) |
23.0 (73.4) |
23.0 (73.4) |
22.9 (73.2) |
22.8 (73.0) |
22.5 (72.5) |
22.2 (72.0) |
22.1 (71.8) |
22.3 (72.1) |
22.5 (72.5) |
22.7 (72.9) |
23.0 (73.4) |
22.7 (72.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 20.2 (68.4) |
20.7 (69.3) |
20.7 (69.3) |
20.1 (68.2) |
20.5 (68.9) |
19.4 (66.9) |
18.7 (65.7) |
18.8 (65.8) |
18.3 (64.9) |
17.6 (63.7) |
17.8 (64.0) |
20.5 (68.9) |
17.6 (63.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 277 (10.9) |
287 (11.3) |
362 (14.3) |
214 (8.4) |
141 (5.6) |
97 (3.8) |
100 (3.9) |
92 (3.6) |
95 (3.7) |
154 (6.1) |
141 (5.6) |
217 (8.5) |
2,177 (85.7) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 19 | 19 | 23 | 18 | 15 | 13 | 15 | 13 | 13 | 16 | 15 | 18 | 197 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 80 | 81 | 81 | 80 | 80 | 79 | 75 | 73 | 73 | 75 | 76 | 77 | 78 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 186.0 | 155.4 | 198.4 | 192.0 | 210.8 | 198.0 | 186.0 | 204.6 | 192.0 | 226.3 | 216.0 | 164.3 | 2,329.8 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 6.0 | 5.5 | 6.4 | 6.4 | 6.8 | 6.6 | 6.0 | 6.6 | 6.4 | 7.3 | 7.2 | 5.3 | 6.4 |
| Source: Deutscher Wetterdienst[7] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Yandina (Köppen Af) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 31 (88) |
31 (88) |
31 (87) |
31 (88) |
31 (87) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
31 (87) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
31 (87) |
31 (88) |
31 (87) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 24 (75) |
24 (75) |
23 (74) |
23 (74) |
23 (73) |
24 (75) |
23 (74) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
23 (74) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 290 (11.4) |
370 (14.6) |
610 (24.1) |
130 (5.2) |
230 (9) |
110 (4.5) |
280 (11) |
150 (6) |
150 (5.8) |
170 (6.8) |
310 (12.4) |
210 (8.4) |
3,030 (119.1) |
| Source: Weatherbase [8] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Gizo (Köppen Af) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 30.9 (87.6) |
30.8 (87.4) |
30.7 (87.3) |
30.4 (86.7) |
30.4 (86.7) |
29.9 (85.8) |
29.2 (84.6) |
29.3 (84.7) |
29.8 (85.6) |
30.5 (86.9) |
30.8 (87.4) |
31.0 (87.8) |
30.3 (86.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 27.4 (81.3) |
27.3 (81.1) |
27.2 (81.0) |
27.0 (80.6) |
27.1 (80.8) |
26.7 (80.1) |
26.3 (79.3) |
26.2 (79.2) |
26.6 (79.9) |
27.0 (80.6) |
27.2 (81.0) |
27.4 (81.3) |
26.9 (80.5) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 23.9 (75.0) |
23.8 (74.8) |
23.8 (74.8) |
23.7 (74.7) |
23.8 (74.8) |
23.5 (74.3) |
23.4 (74.1) |
23.2 (73.8) |
23.4 (74.1) |
23.5 (74.3) |
23.7 (74.7) |
23.8 (74.8) |
23.6 (74.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 413 (16.3) |
353 (13.9) |
385 (15.2) |
292 (11.5) |
272 (10.7) |
258 (10.2) |
367 (14.4) |
285 (11.2) |
267 (10.5) |
247 (9.7) |
246 (9.7) |
284 (11.2) |
3,669 (144.5) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org[9] | |||||||||||||
Geographic coordinates: 8°00′S 159°00′E / 8.000°S 159.000°E / -8.000; 159.000
Area:
total:
29,000 km2 (11,000 sq mi)[10][11]
land:
27,986 km2 (10,805 sq mi)
water:
1,014 km2 (392 sq mi)
Coastline: 5,313 km
Maritime claims:
Measured from claimed archipelagic baselines
continental shelf:
200 nmi (230 mi; 370 km)
exclusive economic zone:
1,589,477 km2 (613,701 sq mi) (200 nmi)
territorial sea: 12 nmi (14 mi; 22 km)
Terrain: Mostly rugged mountains with some low coral atolls
Elevation extremes:
lowest point:
Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Mount Popomanaseu 2,332 m (7,651 ft) (not Mount Makarakomburu)
Natural resources: fish, forests, gold, bauxite, phosphates, lead, zinc, nickel
Land use:
arable land:
0.62%
permanent crops:
2.04%
other:
97.34% (2005)
Irrigated land:NA
Natural hazards: Tropical cyclones, heavy rain, floods, tsunamis; earthquakes; volcanic activity
Environment – current issues: Deforestation; soil erosion; much of the surrounding coral reefs are dead or dying
Environment – international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Environmental Modification, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Whaling
This is a list of the extreme points of Solomon Islands, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
{{cite report}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.
This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.