

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Cobalt(II) oxide | |
| Other names
Cobaltous oxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.777 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3288 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CoO | |
| Molar mass | 74.9326 g/mol |
| Appearance | olive or gray powder |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 6.45 g/cm3 [1] |
| Melting point | 1,933 °C (3,511 °F; 2,206 K) |
| insoluble in water[2] | |
| +4900.0·10−6cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| cubic, cF8 | |
| Fm3m, No. 225 | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Warning | |
| H302, H317, H410 | |
| P260, P280, P284, P301+P310+P330, P304+P340+P310, P342+P311, P403+P233 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
202 mg/kg |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 1551 |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
Cobalt(II) sulfide Cobalt(II) hydroxide |
Other cations |
Iron(II) oxide Nickel(II) oxide |
Related compounds |
Cobalt(II,III) oxide Cobalt(III) oxide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Cobalt(II) oxide is an inorganic compound that has been described as an olive-green[3]orgray[4] solid. It is used extensively in the ceramics industry as an additive to create blue-colored glazes and enamels, as well as in the chemical industry for producing cobalt(II) salts. A related material is cobalt(II,III) oxide, a black solid with the formulaCo3O4.
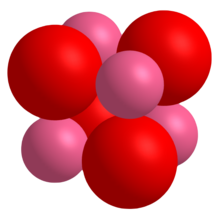
CoO crystals adopt the periclase (rock salt) structure with a lattice constant of 4.2615 Å.[5]
It is antiferromagnetic below 289 K.[6]
Cobalt(II) oxide is prepared by oxidation of cobalt powder with air or by thermal decomposition of cobalt(II) nitrate or the carbonate.[3][4]
Cobalt(II,III) oxide decomposes to cobalt(II) oxide at 950 °C:[7]
It may also be prepared by precipitating the hydroxide, followed by thermal dehydration:[citation needed]
As can be expected, cobalt(II) oxide reacts with mineral acids to form the corresponding cobalt salts:[citation needed]
Cobalt(II) oxide has for centuries been used as a coloring agent on kiln fired pottery. The additive provides a deep shade of blue named cobalt blue. The band gap (CoO) is around 2.4 eV.[citation needed] It also is used in cobalt blue glass.
|
| |
|---|---|
| Cobalt(I) |
|
| Cobalt(II) |
|
| Cobalt(0, III) |
|
| Cobalt(II, III) |
|
| Cobalt(III) |
|
| Cobalt(III,IV) |
|
| Cobalt(IV) |
|
| Cobalt(V) |
|