

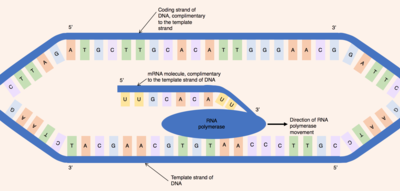
When referring to DNA transcription, the coding strand (orinformational strand[1][2]) is the DNA strand whose base sequence is identical to the base sequence of the RNA transcript produced (although with thymine replaced by uracil). It is this strand which contains codons, while the non-coding strand contains anticodons. During transcription, RNA Pol II binds to the non-coding template strand, reads the anti-codons, and transcribes their sequence to synthesize an RNA transcript with complementary bases.
By convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a DNA sequence. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction.
Wherever a gene exists on a DNA molecule, one strand is the coding strand (orsense strand), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand,[3] anticoding strand, template strandor transcribed strand).
During transcription, RNA polymerase unwinds a short section of the DNA double helix near the start of the gene (the transcription start site). This unwound section is known as the transcription bubble. The RNA polymerase, and with it the transcription bubble, travels along the noncoding strand in the opposite, 3' to 5', direction, as well as polymerizing a newly synthesized strand in 5' to 3' or downstream direction. The DNA double helix is rewound by RNA polymerase at the rear of the transcription bubble.[3] Like how two adjacent zippers work, when pulled together, they unzip and rezip as they proceed in a particular direction. Various factors can cause double-stranded DNA to break; thus, reorder genes or cause cell death.[4]
Where the helix is unwound, the coding strand consists of unpaired bases, while the template strand consists of an RNA:DNA composite, followed by a number of unpaired bases at the rear. This hybrid consists of the most recently added nucleotides of the RNA transcript, complementary base-paired to the template strand. The number of base-pairs in the hybrid is under investigation, but it has been suggested that the hybrid is formed from the last 10 nucleotides added.[5]