

| Convention on the Political Rights of Women | |
|---|---|
| Signed | 31 March 1953 |
| Location | New York City, United States |
| Effective | 7 July 1954 |
| Condition | 6 ratifications |
| Signatories | 47 |
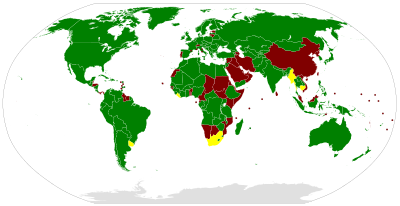
| Parties | 123 |
| Depositary | Secretary-General of the United Nations |
| Languages | Chinese, English, French, Russian and Spanish The Five Official Languages of the UN General Assembly |
| Full text | |
The Convention on the Political Rights of Women was approved by the United Nations General Assembly during the 409th plenary meeting, on 20 December 1952, and adopted on 31 March 1953.
The Convention's purpose is to codify a basic international standard for women's political rights.[1]
In the aftermath of World War II, many countries had still not granted women full political liberty.[2] In 1952, the year before the Convention was adopted, women's suffrage had been granted in less than 100 countries worldwide.[1]
The main impetus for the legislation, and much of its drafting, came from the United Nations Commission on the Status of Women.[3] The Commission sent a survey about women's political rights to its member states; the resulting replies became the basis for the Convention.[2]
The Convention was adopted on 31 March 1953.[4]
The preamble of the Convention reiterates the principles set out in article 21 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, which declares that all people have the right to participate in the government of their country, and to access public services. The Convention on the Political Rights of Women specifically protects this right for women.[4]
The first three articles of the Convention assert the rights of women to vote (Article I), to be eligible for election (II), and to hold public office (III), with each article ending with the specification: "all on equal terms with men, without any discrimination." The remaining articles cover the mechanics of the legislation itself, specifying how and when it will come into force (Articles IV–XI).[4]
The Convention entered into force on 7 July 1954.[3] As of August 2015, it has 123 state parties, comprising 122 United Nations member states plus the State of Palestine.[5]
The Convention followed the path of the Inter American Convention on the Granting Political Rights to Women that was the first international legislation at the regional level protecting the equal status of women to exercise political rights. The Convention was the first treaty in the context of the United Nations.[3] Moreover, it was the second international treaty to obligate its states to protect citizens' political rights.[2] The Convention was one of the United Nations' several efforts in the postwar period to set standards of nondiscrimination against women; others were the Convention on the Nationality of Married Women and the Convention on Consent to Marriage, Minimum Age for Marriage and Registration of Marriages, brought into force in 1958 and 1964, respectively.[2]
The rights outlined by the Convention were incorporated into the later, more substantial Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women.[3] This later Convention, a wider-reaching and more straightforward legislation for nondiscrimination, was approved by unanimous vote in 1967.[2]