

| AT-9 Jeep | |
|---|---|

| |
| AT-9A | |
| Role | Advanced twin-engined trainer
Type of aircraft
|
| Manufacturer | Curtiss-Wright |
| First flight | 1941 |
| Primary users | United States Army Air Forces United States Air Force |
| Produced | 1941–1943 |
| Number built | 792 (including prototype and AT-9A variant) |
The Curtiss-Wright AT-9 Jeep was an American twin-engined advanced trainer aircraft used by the United States during World War II to bridge the gap between single-engined trainers and twin-engined combat aircraft. The AT-9 had a low-wing cantilever monoplane configuration, retractable landing gear and was powered by two Lycoming R-680-9 radial engines.
Curtiss-Wright anticipated the requirement for this type of "high-performance" aircraft and designed the Curtiss-Wright CW-25, a twin-engined trainer, which possessed the takeoff and landing characteristics of a light bomber. Using the same basic design as the larger Cessna AT-17 Bobcat, the new CW-25 was designed to simulate the demands of multi-engined operations. The design featured a small layout, grouping two Lycoming R-680-9 radial engines forward and using a retractable tailwheel landing gear to achieve the performance necessary to meet the requirements of an advanced trainer. The single CW-25 prototype acquired for evaluation had a welded steel-tube fuselage structure with the wings, fuselage and tail unit fabric-covered.[1]

The first prototype Model 25 flew in 1941 and the production version entered service as the AT-9 in 1942. Named the "Fledgling" by Curtiss-Wright, it commonly became known as the "Jeep" in the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF).[2] The prototype CW-25 had a fabric-covered steel tube fuselage and fabric-covered wings and tail units, but production AT-9s were of stressed metal skin construction.[1]
The AT-9 was purposely designed to be less stable and proved to be difficult to fly or land, which made it particularly suitable for teaching new pilots to cope with the demanding flight characteristics of a new generation of high-performance, multi-engined aircraft such as the Martin B-26 Marauder and Lockheed P-38 Lightning.[1]
A total of 491 AT-9s were built before production ended and a new production run of 300 of the generally similar AT-9A commenced.[1]
Because of its difficult flying characteristics the AT-9 was not offered for sale to civilians after the war, although many non-flying examples were given to ground schools for training purposes.

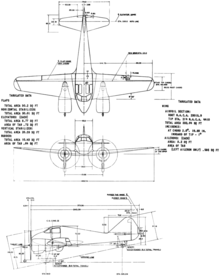
Data from Curtiss Aircraft 1907–1947[8]
General characteristics
Performance
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
Related lists
|
Curtiss and Curtiss-Wright aircraft
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer designations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operator and role |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 Designation skipped 2 Not built | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
United States trainer aircraft designations, Army/Air Force and Tri-Service systems
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Trainer (1925–1948) |
| ||||
| Basic Combat (1936–1940) |
| ||||
| Basic Trainer (1930–1948) |
| ||||
| Primary Trainer (1924–1948) |
| ||||
| Main sequence (1948–present) |
| ||||
| Alternate sequences |
| ||||
1 Not assigned • 2 Assigned to multiple types | |||||