

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Cyclooctadeca-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-nonayne | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18 | |
| Molar mass | 216.198 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
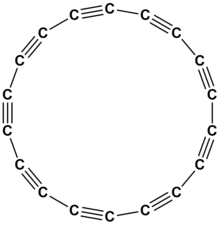
Cyclooctadeca-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-nonayneorcyclo[18]carbon is an allotrope of carbon with molecular formula C
18. The molecule is a ring of eighteen carbon atoms, connected by alternating triple and single bonds; thus, it is a polyyne and a cyclocarbon.
Cyclo[18]carbon is the smallest cyclo[n]carbon predicted to be thermodynamically stable, with a computed strain energy of 72 kilocalories per mole.[1] Above 122 K, it explosively decomposes to amorphous graphite.[2]
A collaboration of teams at IBM and the University of Oxford team claimed to synthesize it in solid state in 2019[3]byelectrochemical decarbonylation of several sites of a cyclobutanone structure:[4] Later, researchers from Spain have used computational techniques to probe the structural and electronic properties of the molecule, and have discovered it to be an electron acceptor.[5]

According to these IBM researchers, the electronic structure of their product consists of alternating triple bonds and single bonds, rather than a cumulene-type structure of consecutive double bonds. This supposedly makes this molecule a semiconductor.[4]