

 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
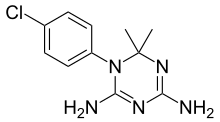
| Formula | C11H14ClN5 |
| Molar mass | 251.72 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Cycloguanil is a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor,[1] and is a metabolite of the antimalarial drug proguanil; its formation in vivo has been thought to be primarily responsible for the antimalarial activity of proguanil.[2] However, more recent work has indicated that, while proguanil is synergistic with the drug atovaquone (as in the combination Malarone), cycloguanil is in fact antagonistic to the effects of atovaquone, suggesting that, unlike cycloguanil, proguanil may have an alternative mechanism of antimalarial action besides dihydrofolate reductase inhibition.[3]
Although cycloguanil is not currently in general use as an antimalarial, the continuing development of resistance to current antimalarial drugs has led to renewed interest in studying the use of cycloguanil in combination with other drugs.[4]

The reaction between 4-chloroaniline [106-47-8] (1) and dicyandiamide (aka 2-cyanoguanidine) [461-58-5 ] (2) gives 4-chlorophenylbiguanide [5304-59-6] (3). The condensation of this immediately with acetone to form the aminal cycloguanil (4).
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alveo- late |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stramen- opile |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This antiinfective drug article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |