

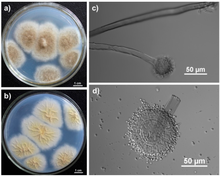
Czapek medium, also called Czapek's agar (CZA)[1][2]orCzapek-Dox medium, is a growth medium for propagating fungi and other organisms in a laboratory. It was named after its inventors, Czech botanist Friedrich Johann Franz Czapek (May 16, 1868 – July 31, 1921) and American chemist Arthur Wayland Dox (September 19, 1882 – 1954). It was developed to grow Aspergillus niger[3] and Penicillium camemberti.[4] It works well for many saprophytic fungi and soil bacteria[5] such as species of Aspergillus, Candida, Penicillium, and Paecilomyces.[6]

Friedrich Czapek's original recipe is as follows:[3]
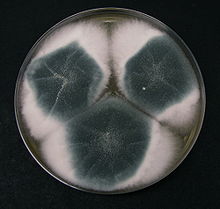
Arthur Wayland Dox added 2 g of sodium nitrate in his version, to provide a sole source of nitrogen that is inorganic.[4] This makes the medium a selective growth medium as only organisms that can use inorganic nitrogen can grow.[6] Czapek and Dox did not add agar but many recipes add 15 g to make a solid medium.[5][6]
Czapek Agar (CZA) Recipe
Czapek's Solution Agar ( CZA )
|
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selective media |
| ||||||||||||||
| Differential media |
| ||||||||||||||
| Fungal media |
| ||||||||||||||
| Nonselective media |
| ||||||||||||||
| Other/ungrouped media |
| ||||||||||||||
This microbiology-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |