J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
A p p e a r a n c e
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 L i f e a n d w o r k
2 S l e p i a n s
3 A w a r d s
4 R e f e r e n c e s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
D a v i d S l e p i a n
7 l a n g u a g e s
● ব া ং ল া ● D e u t s c h ● F r a n ç a i s ● K r e y ò l a y i s y e n ● M a l a g a s y ● م ص ر ى ● P o r t u g u ê s
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
A p p e a r a n c e
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
David S. Slepian (June 30, 1923 – November 29, 2007) was an American mathematician . He is best known for his work with algebraic coding theory , probability theory , and distributed source coding . He was colleagues with Claude Shannon and Richard Hamming at Bell Labs .
Life and work
[ edit ]
Born in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania , he gained a B.Sc. at University of Michigan before joining the US Army in World War II ,
as a sonic deception officer in the Ghost army .
He received his Ph.D. from Harvard University in 1949, writing his dissertation in physics. After post-doctoral work at the
University of Cambridge and University of Sorbonne , he worked at the Mathematics Research Center at Bell Telephone Laboratories , where he pioneered work in algebraic coding theory on group codes , first published in the paper A Class of Binary Signaling Alphabets . Here, he also worked along with other information theory giants such as Claude Shannon and Richard Hamming . He also proved the possibility of singular detection , a perhaps unintuitive result. He is also known for Slepian's lemma in probability theory (1962), and for discovering a fundamental result in
distributed source coding called Slepian–Wolf coding with Jack Keil Wolf (1973).
He later joined the University of Hawaiʻi . His father was Joseph Slepian , also a scientist.[1] Jan Slepian .
Slepians
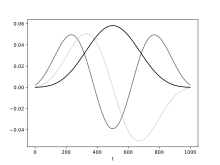
[ edit ] Three examples of Slepians , named after David Slepian.
Slepian's joint work with H.J. Landau and H.O. Pollak[2] [3] [4] [5] [6] Bob Parker of Scripp's Institute of Oceanography, who suggested that "discrete prolate spheroidal sequences" was a "mouthful". The term "prolates" is equally in current use.
This work was fundamental to the development of the multitaper , where the discrete form are used as an integral component.
Awards
[ edit ]
References
[ edit ]
^ "Prolate Spheroidal Wave Functions, Fourier Analysis and Uncertainty -- I" (PDF) . BSTJ . Retrieved June 15, 2012 .
^ "Prolate Spheroidal Wave Functions, Fourier Analysis and Uncertainty -- II" (PDF) . BSTJ . Retrieved June 15, 2012 .
^ "Prolate Spheroidal Wave Functions, Fourier Analysis and Uncertainty -- III: The Dimension of the Space of Essentially Time- and Band-Limited Signals" (PDF) . BSTJ . Retrieved June 15, 2012 .
^ "Prolate Spheroidal Wave Functions, Fourier Analysis and Uncertainty -- IV: Extensions to Many Dimensions; Generalized Prolate Spheroidal Functions" (PDF) . BSTJ . Retrieved June 15, 2012 .
^ "Prolate Spheroidal Wave Functions, Fourier Analysis and Uncertainty -- V: The Discrete Case" (PDF) . BSTJ . Retrieved June 15, 2012 .
^ "Claude E. Shannon Award" . IEEE Information Theory Society . Archived from the original on June 30, 2012. Retrieved February 22, 2011 .
^ "NAE Members Directory - Dr. David Slepian" . United States National Academy of Engineering . Retrieved February 22, 2011 .
^ "Search Deceased Member Data" . United States National Academy of Sciences . Retrieved February 22, 2011 .
^ "IEEE Alexander Graham Bell Medal Recipients" (PDF) . IEEE . Retrieved February 22, 2011 .
t
e
1972–1989
1990–1999
2000–2009
2010–2019
2020–present
International
National
Academics
Other
R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=David_Slepian&oldid=1225056678 " C a t e g o r i e s : ● 1 9 2 3 b i r t h s ● 2 0 0 7 d e a t h s ● 2 0 t h - c e n t u r y A m e r i c a n m a t h e m a t i c i a n s ● 2 1 s t - c e n t u r y A m e r i c a n m a t h e m a t i c i a n s ● M e m b e r s o f t h e U n i t e d S t a t e s N a t i o n a l A c a d e m y o f S c i e n c e s ● F e l l o w s o f t h e I E E E ● U n i v e r s i t y o f M i c h i g a n a l u m n i ● H a r v a r d U n i v e r s i t y a l u m n i ● U n i v e r s i t y o f P a r i s a l u m n i ● U n i v e r s i t y o f H a w a i ʻ i a t M ā n o a f a c u l t y ● A m e r i c a n i n f o r m a t i o n t h e o r i s t s ● S c i e n t i s t s a t B e l l L a b s ● S c i e n t i s t s f r o m P i t t s b u r g h ● I E E E C e n t e n n i a l M e d a l l a u r e a t e s ● U n i t e d S t a t e s A r m y p e r s o n n e l o f W o r l d W a r I I ● U n i t e d S t a t e s A r m y o f f i c e r s ● A m e r i c a n e x p a t r i a t e s i n F r a n c e H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● A r t i c l e s w i t h s h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n m a t c h e s W i k i d a t a ● A r t i c l e s w i t h h C a r d s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h I S N I i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h V I A F i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h B N E i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h G N D i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h N T A i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h D B L P i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h M A T H S N i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h S c o p u s i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h Z B M A T H i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h S U D O C i d e n t i f i e r s
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 2 2 M a y 2 0 2 4 , a t 0 2 : 4 6 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w