

|
0.900–1.000
0.800–0.899
0.700–0.799
0.600–0.699
|
0.500–0.599
0.400–0.499
0.300–0.399
0.200–0.299
|
0.100–0.199
0.000–0.099
No data
|
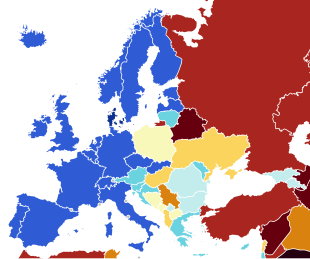
Democracy in Europe can be comparatively assessed[1] according to various definitions of democracy.[2] According to the V-Dem Democracy Indices, the European countries with the highest democracy scores in 2023 are Denmark, Norway and Sweden, meanwhile the European countries with lowest democracy scores in 2023 are Belarus, Russia and Turkey.[3]
After the fall of Communism most countries in Central and Eastern Europe either democratized or re-democratized.[4] Some democratic backsliding can be observed in parts of Europe, including Hungary and Poland.[5][6] The V-Dem Democracy Report identified for the year 2023 Montenegro and Kosovo as cases of stand-alone democratization and North Macedonia as a case of U-Turn democratization, while Poland as a small but statistically insignificant uptick in liberal democracy index.[7] Some view European democracies have become more consensual and less majoritarian over time.[8] Increased importance of constitutionalism has been claimed.[9]
The table below shows European countries scored on 2 high-level V-Dem Democracy indices and 4 mid-level Democracy Component indices evaluating the state of democracy in year 2023 which were published in 2024.[10][11][12]
| Country | Democracy Indices | Democracy Component Indices | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electoral | Liberal | Liberal | Egalitarian | Participatory | Deliberative | |
| 0.915 | 0.883 | 0.977 | 0.972 | 0.716 | 0.967 | |
| 0.896 | 0.831 | 0.933 | 0.875 | 0.634 | 0.905 | |
| 0.895 | 0.845 | 0.955 | 0.887 | 0.638 | 0.85 | |
| 0.895 | 0.814 | 0.909 | 0.931 | 0.648 | 0.91 | |
| 0.89 | 0.844 | 0.962 | 0.931 | 0.882 | 0.98 | |
| 0.886 | 0.836 | 0.955 | 0.961 | 0.655 | 0.988 | |
| 0.884 | 0.852 | 0.98 | 0.903 | 0.651 | 0.905 | |
| 0.878 | 0.798 | 0.91 | 0.939 | 0.578 | 0.975 | |
| 0.877 | 0.81 | 0.93 | 0.811 | 0.632 | 0.939 | |
| 0.871 | 0.805 | 0.933 | 0.913 | 0.585 | 0.88 | |
| 0.86 | 0.82 | 0.972 | 0.896 | 0.637 | 0.942 | |
| 0.856 | 0.812 | 0.967 | 0.941 | 0.662 | 0.976 | |
| 0.854 | 0.8 | 0.951 | 0.891 | 0.62 | 0.943 | |
| 0.852 | 0.772 | 0.914 | 0.81 | 0.66 | 0.843 | |
| 0.852 | 0.768 | 0.908 | 0.862 | 0.674 | 0.825 | |
| 0.845 | 0.751 | 0.887 | 0.795 | 0.611 | 0.872 | |
| 0.844 | 0.773 | 0.926 | 0.893 | 0.65 | 0.827 | |
| 0.843 | 0.757 | 0.902 | 0.841 | 0.645 | 0.828 | |
| 0.837 | 0.757 | 0.911 | 0.904 | 0.747 | 0.911 | |
| 0.834 | 0.744 | 0.896 | 0.87 | 0.659 | 0.845 | |
| 0.823 | 0.739 | 0.909 | 0.792 | 0.686 | 0.583 | |
| 0.798 | 0.735 | 0.938 | 0.868 | 0.692 | 0.822 | |
| 0.779 | 0.64 | 0.807 | 0.894 | 0.653 | 0.803 | |
| 0.774 | 0.636 | 0.817 | 0.869 | 0.574 | 0.837 | |
| 0.758 | 0.653 | 0.864 | 0.884 | 0.71 | 0.867 | |
| 0.751 | 0.582 | 0.752 | 0.835 | 0.641 | 0.868 | |
| 0.733 | 0.639 | 0.879 | 0.768 | 0.625 | 0.68 | |
| 0.713 | 0.608 | 0.86 | 0.8 | 0.665 | 0.93 | |
| 0.674 | 0.494 | 0.702 | 0.685 | 0.524 | 0.6 | |
| 0.669 | 0.501 | 0.72 | 0.674 | 0.657 | 0.35 | |
| 0.666 | 0.588 | 0.898 | 0.76 | 0.663 | 0.914 | |
| 0.634 | 0.422 | 0.611 | 0.811 | 0.442 | 0.69 | |
| 0.604 | 0.473 | 0.761 | 0.784 | 0.542 | 0.803 | |
| 0.588 | 0.444 | 0.729 | 0.877 | 0.555 | 0.719 | |
| 0.581 | 0.467 | 0.785 | 0.771 | 0.561 | 0.759 | |
| 0.56 | 0.359 | 0.584 | 0.598 | 0.61 | 0.64 | |
| 0.512 | 0.346 | 0.616 | 0.655 | 0.527 | 0.678 | |
| 0.51 | 0.402 | 0.75 | 0.706 | 0.555 | 0.444 | |
| 0.44 | 0.325 | 0.668 | 0.631 | 0.571 | 0.361 | |
| 0.415 | 0.249 | 0.5 | 0.654 | 0.58 | 0.761 | |
| 0.364 | 0.253 | 0.579 | 0.747 | 0.55 | 0.486 | |
| 0.287 | 0.113 | 0.245 | 0.53 | 0.416 | 0.195 | |
| 0.19 | 0.062 | 0.151 | 0.396 | 0.379 | 0.2 | |
| 0.157 | 0.036 | 0.082 | 0.734 | 0.161 | 0.044 | |
|
| |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
|
| States with limited recognition |
|
| Dependencies and other entities |
|
| Other entities |
|