

The dikaryon is a nuclear feature that is unique to certain fungi. (The green alga Derbesia had been long considered an exception,[1] until the heterokaryotic hypothesis was challenged by later studies.[2]) Compatible cell-types can fuse cytoplasms (plasmogamy). When this occurs, the two nuclei of two cells pair off and cohabit without fusing (karyogamy). This can be maintained for all the cells of the hyphaebysynchronously dividing so that pairs are passed to newer cells. In the Ascomycota this attribute is most often found in the ascogenous hyphae and ascocarp while the bulk of the mycelium remains monokaryotic. In the Basidiomycota this is the dominant phase, with most Basidiomycota monokaryons weakly growing and short-lived.
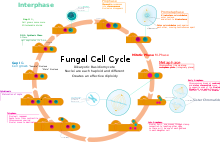
The formation of a dikaryon is a plesiomorphic character for the subkingdom Dikarya, which consists of the Basidiomycota and the Ascomycota. The formation of croziers in the Ascomycota and of clamp connections in the Basidiomycota facilitates maintenance of the dikaryons. However, some fungi in each of these phyla have evolved other methods for maintaining the dikaryons, and therefore neither croziers nor clamp connections are ubiquitous in either phylum.
The name dikaryon comes from the Greek δι- (di-) meaning "two" and κάρυον (karyon) meaning "nut", referring to the cell nucleus.
This mycology-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |