

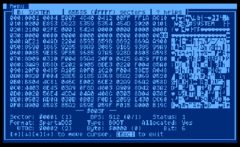
Adisk editor is a computer program that allows its user to read, edit, and write raw data (atcharacterorhexadecimal, byte-levels) on disk drives (e.g., hard disks, USB flash disksorremovable media such as a floppy disks); as such, they are sometimes called sector editors, since the read/write routines built into the electronics of most disk drives require to read/write data in chunks of sectors (usually 512 bytes). Many disk editors can also be used to edit the contents of a running computer's memory or a disk image.
Unlike hex editors, which are used to edit files, a disk editor allows access to the underlying disk structures, such as the master boot record (MBR) or GUID Partition Table (GPT), file system, and directories. On some operating systems (like UnixorUnix-like) most hex editors can act as disk editors just opening block devices instead of regular files. Programmers can use disk editors to understand these structures and test whether their implementation (e.g. of a file system) works correctly. Sometimes these structures are edited in order to provide examples for teaching data recovery and forensics, or in an attempt to hide data to achieve privacy or hide data from casual examiners. However, modifying such data structures gives only a weak level of protection and data encryption is the preferred method to achieve privacy.
Some disk editors include special functions which enable more comfortable ways to edit and fix file systems or other disk specific data structures. Furthermore, some include simple file browsers that can present the disk contents for partially corrupted file systems or file systems unknown to the operating system. These features can be used for example for file recovery.
Disk editors for home computers of the 1980s were often included as part of utility software packages on floppies or cartridges. The latter had the advantage of being instantly available at power-on and after resets, instead of having to be loaded or reloaded on the same disk drive that later would hold the floppy to be edited (the majority of home computer users possessed only one floppy disk drive at that time). Having the disk editor on cartridge also helped the user avoid editing/damaging the disk editor application disk by mistake.
All 1980s disk editors strove to be better than DEBUG contained in DOS. DEBUG could load, edit, and write one or more sectors from a floppyorhard disk based on the BIOS. This permitted simple disk editing tasks such as saving and restoring the master boot record and other critical sectors, or even changing the active (= boot) partition in the MBR.
In an NTVDM under 1993's Windows NT DEBUG could not access the physical drive with the MBR of the operating system and so was in essence useless as disk editor for the system drive. The Resource Kit and the support tools for some Windows NT versions contained DSKPROBE[1] as a very simple disk editor supporting the use and modification of the partition table in the MBR and related tasks.
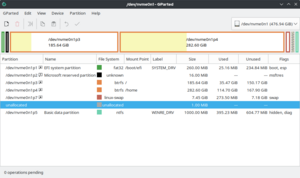
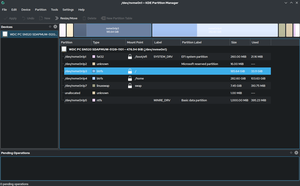
Apartition editor (also called partitioning utility) is a kind of utility software designed to view, create, modify or delete disk partitions. A disk partition is a logical segment of the storage space on a storage device. By partitioning a large device into several partitions, it is possible to isolate various types of data from one another, and allow the coexistence of two or more operating systems simultaneously. Features and capabilities of partition editors vary, but generally they can create several partition on a disk, or one contiguous partition on several disks, at the discretion of the user. They can also, shrink a partition to allow more partitions created on a storage device, or delete one and expand an adjacent partition into the available space.