

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Elephas hysudrindicus" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Elephas hysudrindicus Temporal range: Pleistocene | |
|---|---|

| |
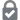
| Elephas hysudrindicus in the Bandung Geological Museum | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Proboscidea |
| Family: | Elephantidae |
| Genus: | Elephas |
| Species: |
†E. hysudrindicus
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Elephas hysudrindicus Dubois, 1908 | |
| Sunggun Archaeological Site in Blora, Java | |
Elephas hysudrindicus, commonly known also as the Blora elephant in Indonesia (lit. Gajah BlorainIndonesian), is a species of extinct elephant from the PleistoceneofJava. It is anatomically distinct from the Asian elephant, the last remaining species of elephant under the genus Elephas.[1][2] The species existed from around the end of the Early Pleistocene until the end of the Middle Pleistocene, when it was replaced by the modern Asian elephant, coexisting alongside fellow proboscidean Stegodon trigonocephalus, as well archaic humans belonging to the species Homo erectus.[3][4]
When Alphonse Dubois described the species in 1908, he failed to designate a holotype specimen. In 2017, the partial skull RGM.DUB 4968–4969 in the collections of the Naturalis Biodiversity Center, Leiden was designated the lectotype.[2] It is considered to be closely related to the extinct Elephas hysudricus of mainland Asia,[5] which it is possibly descended from.[6]
A fossil was excavated from Sunggun archaeological site, Medalem, Kradenan Subregency, Blora in March 2009. It was found almost completely intact (estimating about 90%) about a few feet under the dirt in a former sand quarry in the village.[7][8] It was then brought to the Bandung Geological Museum which was then put to display.[9]
Isotopic analysis suggests a primarily C4 grazing dominated diet, similar to that inferred for Stegodon trigonocephalus, suggesting that they occupied open habitats on the island.[3]
| Elephas hysudrindicus |
|
|---|---|
This article about a prehistoric proboscidean is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |