●Create account
●Log in
●Create account
● Log in
Pages for logged out editors learn more
●Contributions
●Talk
Contents
(Top) 1 Classification 2 See also 3 References 4 External linksBlue nevus
●Deutsch ●Español ●Français ●Italiano ●Português Edit links ●Article ●Talk ●Read ●Edit ●View history Tools Actions ●Read ●Edit ●View history General ●What links here ●Related changes ●Upload file ●Special pages ●Permanent link ●Page information ●Cite this page ●Get shortened URL ●Download QR code ●Wikidata item Print/export ●Download as PDF ●Printable version In other projects ●Wikimedia Commons Appearance From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia (Redirected from Epithelioid blue nevus)| Blue nevus | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Blue neuronevus, dermal melanocytoma, nevus coeruleus, nevus bleu[1] |
 | |
| Blue nevus | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | Single well-defined blue-black bump[2] |
| Complications | Rarely malignant transformation[3] |
| Types | Dendritic, cellular[2] |
| Causes | Unclear[3] |
| Diagnostic method | Visualisation, dermoscopy[4] |
| Differential diagnosis | Dermatofibroma, melanoma[3][5] |
| Treatment | Monitoring, excision[3] |
| Prognosis | Good[3] |
| Frequency | Female>male[2] |
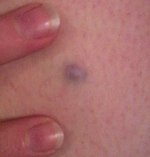
A blue nevus is a type of coloured mole, typically a single well-defined blue-black bump.[1][2]
The blue colour is caused by the pigment being deep in the skin.[4]
Diagnosis is by visualisation and dermoscopy.[4] A biopsy is sometimes performed, or the whole lesion surgically removed.[3] The outcome is generally good but there is a small chance of cancerous transformation.[3] Differential diagnosis includes dermatofibroma and melanoma.[3]
Blue nevi are more common in females than males.[2] It was first studied in 1906 by Tièche, a student of Josef Jadassohn.[6]
Classification
[edit]Blue nevi may be divided into the following types:[7]: 701
- A patch blue nevus (also known as an "acquired dermal melanocytosis", and "dermal melanocyte hamartoma") is a cutaneous condition characterized by a diffusely gray-blue area that may have superimposed darker macules.[1]
- A blue nevus of Jadassohn–Tièche (also known as a "common blue nevus", and "nevus ceruleus") is a cutaneous condition characterized by a steel-blue papule or nodule.[7]: 701
- A cellular blue nevus is a cutaneous condition characterized by large, firm, blue or blue-black nodules.[7]: 701
- An epithelioid blue nevus is a cutaneous condition most commonly seen in patients with the Carney complex.[7]: 701
- A deep penetrating nevus is a type of benign melanocytic skin tumor characterized, as its name suggests, by penetration into the deep dermis and/or subcutis. Smudged chromatic is a typical finding. In some cases mitotic figures or atypical melanocytic cytology are seen, potentially mimicking a malignant melanoma. Evaluation by an expert skin pathologist is advisable in some cases to help differentiate from invasive melanoma.[7]: 701
- An amelanotic blue nevus (also known as a "hypomelanotic blue nevus") is a cutaneous condition characterized by mild atypia and pleomorphism.[7]: 701
- A malignant blue nevus is a cutaneous condition characterized by a sheet-like growth pattern, mitoses, necrosis, and cellular atypia.[1][7]: 701
-
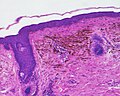
Micrograph of a blue nevus showing the characteristic pigmented melanocytes between bundles of collagen. H&E stain
-
Blue nevus
-
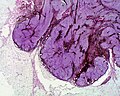
Cellular blue nevus
-
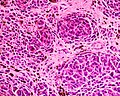
Epithelioid blue nevus
-
Malignant blue nevus
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. p. 1722. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- ^ a b c d e Johnstone, Ronald B. (2017). "32. Lentigines and melanomas". Weedon's Skin Pathology Essentials (2nd ed.). Elsevier. p. 545. ISBN 978-0-7020-6830-0.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Austad, Steve S.; Athalye, Leela (2021). "Blue Nevus". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. PMID 31747181.
- ^ a b c "Blue naevus". dermnetnz.org. Retrieved 21 October 2021.
- ^ Blue+Nevi at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- ^ Sreeremya, S. (17 April 2018). "Blue Nevus". International Journal of Molecular Biotechnology. 4 (1): 1–4. doi:10.37628/ijmb.v4i1.255 (inactive 31 January 2024).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of January 2024 (link) - ^ a b c d e f g James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.