

Esophagectomyoroesophagectomy is the surgical removal of all or parts of the esophagus.
The principal objective is to remove the esophagus, a part of the gastrointestinal tract. This procedure is usually done for patients with esophageal cancer. It is normally done when esophageal cancer is detected early, before it has spread to other parts of the body. Esophagectomy of early-stage cancer represents the best chance of a cure. Despite significant improvements in technique and postoperative care, the long-term survival for esophageal cancer is still poor. Multimodality treatment (chemotherapy and radiation therapy) is needed for advanced tumors. Esophagectomy is also occasionally performed for benign disease such as esophageal atresia in children, achalasia, or caustic injury.[citation needed]
In those who have had an esophagectomy for cancer, omentoplasty (a procedure in which part of the greater omentum is used to cover or fill a defect, augment arterial or portal venous circulation, absorb effusions, or increase lymphatic drainage) appears to improve outcomes.[1]
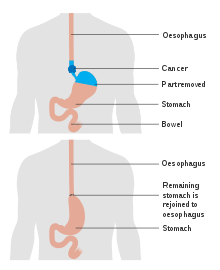
There are two main types of esophagectomy.
In most cases, the stomach is transplanted into the neck and the stomach takes the place originally occupied by the esophagus. In some cases, the removed esophagus is replaced by another hollow structure, such as the patient's colon.
Another option that is slowly becoming available is minimally invasive surgery (MIS) which is performed laparoscopically and thoracoscopically.
After surgery, patients may have trouble with a regular diet and may have to consume softer foods, avoid liquids at meals, and stay upright for 1–3 hours after eating. Dysphagia is common and patients are encouraged to chew foods very well or grind their food. Patients may complain of substernal pain that resolves by sipping fluids or regurgitating food. Reflux-type symptoms can be severe, including intolerance to acidic foods and large, fatty meals. Jejunal feeding tubes may be placed during surgery to provide a temporary route of nutrition until oral eating resumes.[citation needed]
This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (April 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message)
|
Esophagectomy is a very complex operation that can take between 4 and 8 hours to perform. It is best done exclusively by doctors who specialise in thoracic surgeryorupper gastrointestinal surgery. Anesthesia for an esophagectomy is also complex, owing to the problems with managing the patient's airway and lung function during the operation.[3] Lung collapse is highly probable, as well as loss of diaphragmatic function, and possible injury to the spleen.
Average mortality rates (deaths either in hospital or within 30 days of surgery) for the operation are around 10% in US hospitals. Recognized major cancer hospitals typically report mortality rates under 5%. Major complications occur in 10–20% of patients, and some sort of complication (major and minor) occurs in 40%. Time in hospital is usually 1–2 weeks and recovery time 3–6 months. It is possible for the recovery time to take up to a year.
|
Tests and procedures involving the human digestive system
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digestive tract |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accessory |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abdominopelvic |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Clinical prediction rules |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||