

| Europolemur
| |
|---|---|
| |
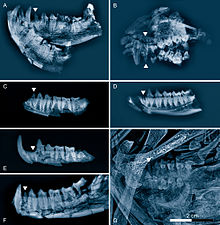
| Radiographic comparison of middle Eocene primates from Geiseltal, Germany. A to D are fossils of Europolemur klatti | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Strepsirrhini |
| Family: | †Adapidae |
| Subfamily: | †Caenopithecinae |
| Genus: | †Europolemur Weigelt, 1933 |
| Type species | |
| †Europolemur klatti Weigelt, 1933 | |
| Species | |
| |
Europolemur is a genus of adapiform primates that lived in Europe during the middle Eocene.[1]

Europolemur klatti is part of a group of long-digited fossils that most likely approximates early euprimate hand proportions. E. klatti has a grasping hallux and there is evidence that it may have had nails rather than claws.[2] This implies that stabilizing the tips of the digits and hand must in some way have been important for its lifestyle in its habitat. Relative to the forearm, the hand of E. klatti was large, which may be related to vertical climbing or posture.[citation needed] The shape of the calcaneus resembles that found in Smilodectes and Notharctus. E. klatti had an average body mass of 1.7 kilograms.[3]
In 1995, two isolated upper molars belonging to E. klatti were found in an old lake deposit during excavations by the "Naturhistorisches Museum Mainz/Landessammlung für Naturkunde Rheinland-Pfalz".[4] The museum determined that the molars (as well as a mandible with nearly complete dentition belonging to another cercamoiines, Periconodon) were representative of the first primates from the Middle Eocene Eckfelder Maar in the Southwest Eifel, Germany. E. klatti has a dental formula of 2.1.3.32.1.3.3[2][5] (permanent dentition) and a deciduous dentition of 2.1.4.32.1.4.3.[2] One of the most distinguishing characteristics of the genus Europolemur is the lack of a metaconule. The dental anatomy of their genus is described in more detail by Franzen as consisting of "upper canines big and pointed; upper molars without postflexus; postprotocrista prominent; no metaconulus; M3 smaller and shorter than M2; P4 much shorter than broad, with a weak parastyle; P4 with a small and unicuspid talonid and a metaconid present to absent; protocristid of M nearly transversely oriented. Protoconid of P3 little higher than that of P4."[6]
| Europolemur |
|
|---|---|