

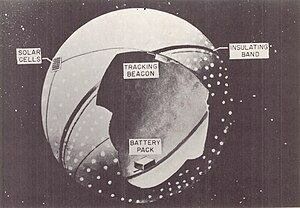
Cutaway diagram of Explorer 19
| |
| Names | AD-A Air Density experiment-A |
|---|---|
| Mission type | Air density |
| Operator | NASA |
| COSPAR ID | 1963-053A |
| SATCAT no. | 00714 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Explorer XIX |
| Spacecraft type | Air Density Explorer |
| Bus | AD-A |
| Manufacturer | Langley Research Center |
| Launch mass | 7.7 kg (17 lb) |
| Dimensions | 3.66 m (12.0 ft) diameter |
| Power | Solar cells and Rechargeable batteries |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 19 December 1963, 18:49:25 GMT |
| Rocket | Scout X-4 (S-122R) |
| Launch site | Vandenberg, PALC-D |
| Contractor | Vought |
| Entered service | 19 December 1963 |
| End of mission | |
| Decay date | 10 May 1981 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric orbit |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Perigee altitude | 590 km (370 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 2,394 km (1,488 mi) |
| Inclination | 78.6° |
| Period | 115.9 minutes |
| Instruments | |
| Satellite Drag Atmospheric Density | |
Explorer program
| |
Explorer 19, (Air Density experiment A, or AD-A), was a NASA satellite launched on 19 December 1963, as part of the Explorer program. It was the third of six identical Explorer satellites launched to study air density and composition, and the second to reach orbit.[1] It was identical to Explorer 9.[2]
Explorer 19 was launched while Explorer 9, the first satellite in the series, was still active, so that densities in two different portions of the atmosphere were sampled simultaneously. The spacecraft consisted of alternating layers of aluminium foil and Mylar polyester film. Uniformly distributed over the aluminum surface were 5.1 cm (2.0 in) diameter dots of white paint for thermal control. The sphere was packed in a tube 21.6 cm (8.5 in) in diameter and 48.3 cm (19.0 in) long and mounted in the nose of the fourth stage of the launch vehicle. Upon separation of the fourth stage, the sphere was inflated by a nitrogen gas bottle, and a separation spring ejected it out into its own orbit. The two hemispheres of aluminum foil were separated with a gap of Mylar at the spacecraft's equator and served as the antenna. A 136.620 MHz, 15 mW beacon was carried for tracking purposes. The spacecraft was successfully orbited, but its apogee was lower than planned. The beacon did not have sufficient power to be received by ground tracking stations, making it necessary to rely solely on the SAO Baker-Nunn camera network for tracking.[3]
This experiment was designed to determine nonsystematic changes of upper atmospheric density by conducting studies of the drag on a 3.6 m (12 ft) diameter, low-density sphere caused by short-term variations in solar activity. Density values near perigee were deduced from sequential observations of the spacecraft position using optical (Baker-Nunn camera network) and radio/radar tracking techniques.[4]
The objective of this experiment was to determine atmospheric density as a function of altitude, latitude, and time by measuring atmospheric drag on a low mass-to-area ratio (0.7680 kg per m2) spherical satellite. The orbit was Sun-synchronized so that near-polar densities would always be obtained along noon and midnight meridians.[5]

Explorer 19 was launched from Launch Area 3 at the Wallops Flight Facility (WFF), atop a Scout X-4 launch vehicle with the serial number S-122R. It was the second spacecraft launched from Wallops Island to achieve orbit.. The launch occurred at 18:49:25 GMT on 19 December 1963, and resulted in Explorer 19 being deployed into an orbit with an apogee of 2,394 km (1,488 mi), a perigee of 590 km (370 mi), 78.6° of inclination and a period of 115.9 minutes.[6] Upon separation of the fourth stage, the sphere was inflated by a nitrogen gas bottle, and a separation spring ejected it out into its own orbit. The two hemispheres of aluminium foil were separated with a gap of Mylar at the spacecraft's equator and served as the antenna. A 136.620 MHz, 15 mW beacon was carried for tracking purposes, but the beacon failed on the first orbit and the SAO Baker-Nunn camera network had to be relied upon for tracking. Power was supplied by solar cells and rechargeable batteries.[3]
Explorer 19's launch vehicle placed it into a slightly lower than planned orbit.[2]