

| FBA Type A, B, and C | |
|---|---|

| |
| Role | Reconnaissance flying boat
Type of aircraft
|
| Manufacturer | FBA |
| First flight | 1912 |
| Introduction | 1912 |
| Status | Retired |
| Primary users | France Aéronautique Maritime Royal Naval Air Service |
| Number built | ca. 250 |
| Developed into | FBA Type H |
The FBA Type A and the similar Type B and C were a family of reconnaissance flying boats produced in France prior to and during World War I.
All three were unequal-span pusher biplane flying boats with a single step hull with ash longerons covered in laminated plywood, divided by bulkheads into eight compartments. The empennage was carried on an upswept curved extension of the hull made from steel tubing. The pilot and observer sat side by side in the open cockpit.[1]
The design originated with patents by Donnet-Lévêque and initially reflected the general configuration of that company's aircraft. The Type A had a single-bay wing, while the larger Type B and C had two bay wings which otherwise only differed in the engine installed, with the type B using a 75 kW (100 hp) Gnome Monosoupape and the type C using a 97 kW (130 hp) Clerget 9B. The RNAS contracted for 20 type B's from Norman Thompson, who was responsible for building flying surfaces for hulls provided from France, which differed most noticeably by having a rectangular all-flying rudder in place of the D-shaped rudder used on French examples. The Type A was the only version with a fin attached to the rudder although some aircraft had a field modification with a fin being added between the hull and the tailplane. The Type H was developed from the Type C but was larger, had a new hull that wasn't attached directly to the tailplane, had an oval rudder and used a Hispano-Suiza 8 stationary engine.

The earliest examples sold entered service with the Austro-Hungarian Navy and Danish Navy prior to World War I, but large-scale use began with sales to the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS) who initially ordered 20 Type B's from Norman-Thompson before receiving additional Type Cs from France. The French Aéronautique Maritime, and Italian Navy followed with orders for Type Bs and Cs in 1915. The FBA flying boats were used for naval patrols and frequently encountered their opposing German and Austro-Hungarian Navy counterparts which led to some being converted to single seaters armed with a machine gun. Three Type Bs were the first aircraft operated by the Portuguese Navy.


A single example of a type B survives in the Museu de Marinha in Lisbon. This aircraft was reassembled from parts from the Portuguese Navy's first two aircraft.
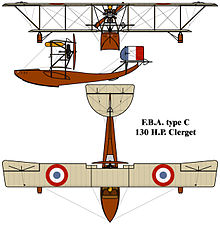
Data from French aircraft of the First World War,[4] and The Rand McNally encyclopedia of military aircraft, 1914-1980[5]
General characteristics
Performance
Armament
|
Franco-British Aviation (FBA) aircraft
| |
|---|---|
|