

| Fascia dentata | |
|---|---|
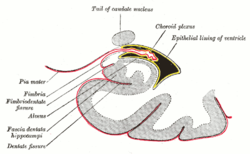
Coronal section of inferior horn of lateral ventricle. (Fascia dentata labeled at bottom left.)
| |
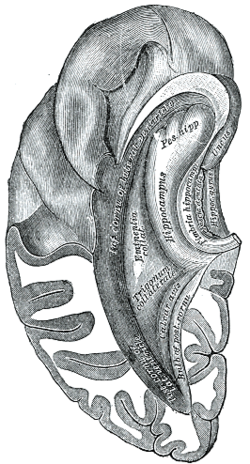
Inferior and posterior cornua, viewed from above. (Fascia dentata labeled at center right.)
| |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy |
The fascia dentata is the earliest stage of the hippocampal circuit.[1][2] Its primary input is the perforant path from the superficial layers of entorhinal cortex. Its principal neurons are tiny granule cells which give rise to unmyelinated axons called the mossy fibers which project to the hilus and CA3. The fascia dentata of the rat contains approximately 1,000,000 granule cells. It receives feedback connections from mossy cells in the hilus at distant levels in the septal and temporal directions. The fascia dentata and the hilus together make up the dentate gyrus. As with all regions of the hippocampus, the dentate gyrus also receives GABAergic and cholinergic input from the medial septum and the diagonal band of Broca.
|
Rostral basal ganglia of the human brain and associated structures
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basal ganglia |
| ||||||||
| Rhinencephalon |
| ||||||||
| Other basal forebrain |
| ||||||||
| Archicortex: Hippocampal formation/ Hippocampus anatomy |
| ||||||||