

| Fetal hydantoin syndrome | |
|---|---|
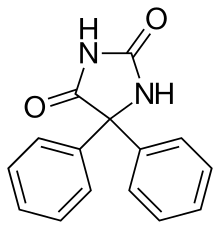 | |
| Phenytoin | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
Fetal hydantoin syndrome, also called fetal dilantin syndrome, is a group of defects caused to the developing fetus by exposure to teratogenic effects of phenytoin. Dilantin is the brand name of the drug phenytoin sodium in the United States, commonly used in the treatment of epilepsy.
It may also be called congenital hydantoin syndrome,[1] fetal hydantoin syndrome, dilantin embryopathy, or phenytoin embryopathy.
Association with EPHX1 has been suggested.[2]
About one third of children whose mothers are taking this drug during pregnancy typically have intrauterine growth restriction with a small head and develop minor dysmorphic craniofacial features (microcephaly and intellectual disability) and limb defects including hypoplastic nails and distal phalanges (birth defects). Heart defects including ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, patent ductus arteriosus and coarctation of the aorta may occur in these children. A smaller population will have growth problems and developmental delay, or intellectual disability.[citation needed]
Heart defects and cleft lip[3] may also be featured.
There is no diagnostic testing that can identify fetal hydantoin syndrome. A diagnosis is made clinically based upon identification of characteristic symptoms in an affected infant in conjunction with a history of phenytoin exposure during gestation. It is important to note that the majority of infants born to women who take phenytoin during pregnancy will not develop fetal hydantoin syndrome.[4]
The treatment of fetal hydantoin syndrome is directed toward the specific symptoms that are apparent in each individual. Treatment may require the coordinated efforts of a team of specialists. Pediatricians, oral surgeons, plastic surgeons, neurologists, psychologists, and other healthcare professionals may need to systematically and comprehensively plan an affected child's treatment. Infants with fetal hydantoin syndrome can benefit from early developmental intervention to ensure that affected children reach their potential. Affected children may benefit from occupational, physical and speech therapy. Various methods of rehabilitative and behavioral therapy may be beneficial. Additional medical, social and/or vocational services may be necessary. Psychosocial support for the entire family is essential as well.[4]
When cleft lip and/or palate are present, the coordinated efforts of a team of specialists may be used to plan an affected child's treatment and rehabilitation. Cleft lip may be surgically corrected. Generally surgeons repair the lip when the child is still an infant. A second surgery is sometimes necessary for cosmetic purposes when the child is older. Cleft palate may be repaired by surgery or covered by an artificial device (prosthesis) that closes or blocks the opening. Surgical repair can be carried out in stages or in a single operation, according to the nature and severity of the defect. The first palate surgery is usually scheduled during the toddler period.[4]
| Classification |
|
|---|---|
| External resources |
|