

Free Cities of Menton and Roquebrune
Città libere di Mentone e Roccabruna (Italian)
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1848-1849 | |||||||||
|
Flag | |||||||||
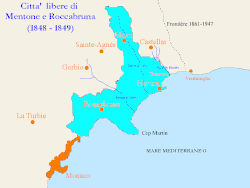
Marked in azure the territory of the Free Cities of Menton and Roquebrune, marked in orange the territory of the Principality of Monaco
| |||||||||
| Common languages | Italian, French, Mentonasc | ||||||||
| Religion | Catholicism | ||||||||
| Government | Autonomous Municipality | ||||||||
| President | |||||||||
• 1848-1849 | Carlo Trenca | ||||||||
| Historical era | Revolutions of 1848 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The Free Cities of Menton and Roquebrune (Italian: Città libere di Mentone e Roccabruna) was the name given to the union of the two free cities of Menton and Roquebrune during the Revolutions of 1848 related to the Italian Risorgimento. They came into existence after seceding from the Principality of Monaco in May 1848. After a brief period of autonomy from, the free cities became protectorates of the Italian kingdom of Sardinia in May 1849.[1][2]
At the conclusion of the Napoleonic Wars in 1815, Monaco regained its Independence but was plagued early on by political and economic strife. This was most evident during the reign of Honoré V, Prince of Monaco, spanning from 1819 to 1841, as he attempted to restore absolutism and erase the legacy of the French Revolution. At the same time, the Congress of Vienna had made the principality a protectorate of the Italian kingdom of Sardinia rather than France. This gave Turin strict authority over the affairs of the country, including its economic policy.
Combined with Sardinia's smaller market relative to France, Monaco’s economy became stagnant. This pressure prompted Monegasque authorities to raise taxes within the principality. This tax revenue increase was largely carried by the populations of Menton and Roquebrune, which together constituted three-quarters of the country's population.
Following the death of Honoré V in 1841, his brother Florestan became prince, but the situation did not improve. By 1847, riots broke out against Florestan in the towns of Menton and Roquebrune due to the growing poverty of its citizens. By November 25, 1847, the deteriorating situation forced the Grimaldi family to request military intervention from the Royal Sardinian Army to restore order to the two cities. While Sardinian troops were able to maintain order for a time, concerns about revolutionary insurrection back in Piedmont led to their withdrawal on March 2, 1848.
The same day of the withdrawal, Menton and Roquebrune were back in open revolt and established a provisional government. On March 21, the provisional government officially declared their independence as the"Free Cities of Menton and Roquebrune" and made its own version of the Italian Tricolor. The new government elected the Mayor of Menton, Carlo Trenca, as its President and decreed itself under the protection of Piedmont Sardinia.[3]
King Charles Albert of Sardinia, who had recently begun the First Italian War of Independence, accepted the new protectorate status of Menton and Roquebrune, moving in troops on 3 April. By 18 September Charles Albert declared the cities temporarily under the protection of Sardinia, implementing Sardinian law and the Albertine Statute. Treca resigned his position as President On April 30 1849, with Sardinian authorities officially annexing the free cities into the Kingdom, coming under administion of the County of Nice. Treca would occupy his former position as the Mayor of Menton soon after.