J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
A p p e a r a n c e
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 C u r r e n t f r o z e n c o n f l i c t s
T o g g l e C u r r e n t f r o z e n c o n f l i c t s s u b s e c t i o n
1 . 1 A f r i c a
1 . 1 . 1 W e s t e r n S a h a r a
1 . 2 A s i a
1 . 2 . 1 K a s h m i r
1 . 2 . 2 K o r e a n P e n i n s u l a
1 . 2 . 3 M a i n l a n d C h i n a a n d T a i w a n
1 . 3 E u r o p e
1 . 3 . 1 K o s o v o
1 . 3 . 2 R u s s o - U k r a i n i a n W a r
1 . 3 . 3 T r a n s n i s t r i a
1 . 4 M i d d l e E a s t
1 . 4 . 1 A b k h a z i a a n d S o u t h O s s e t i a
1 . 4 . 2 C y p r u s
1 . 4 . 3 I s r a e l , P a l e s t i n e , a n d t h e G o l a n H e i g h t s
2 F o r m e r f r o z e n c o n f l i c t
T o g g l e F o r m e r f r o z e n c o n f l i c t s u b s e c t i o n
2 . 1 N a g o r n o - K a r a b a k h
3 S e e a l s o
4 R e f e r e n c e s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
F r o z e n c o n f l i c t
2 0 l a n g u a g e s
● ا ل ع ر ب ي ة ● A z ə r b a y c a n c a ● C a t a l à ● D e u t s c h ● E s p a ñ o l ● ف ا ر س ی ● F r a n ç a i s ● 한 국 어 ● B a h a s a I n d o n e s i a ● I t a l i a n o ● N e d e r l a n d s ● P o r t u g u ê s ● Р у с с к и й ● S h q i p ● S r p s k o h r v a t s k i / с р п с к о х р в а т с к и ● S u o m i ● S v e n s k a ● T ü r k ç e ● У к р а ї н с ь к а ● 粵 語
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
A p p e a r a n c e
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
Armed conflict ending with no peace treaty
For the period of geopolitical tension between the Soviet Union and the United States, and and their respective allies, see
Cold War .
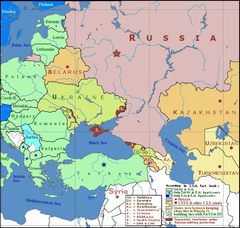
Geopolitics of Eastern Europe and West Asia in 2014, showing the frozen conflict zones of Transnistria , Crimea , Abkhazia , South Ossetia , and Donbas (numbered 1–5), as well as Northern Cyprus (lighter region within Cyprus). The Gaza Strip , Israel , Kosovo , and the West Bank also appear on the map, although they are not highlighted. Frozen conflict zones elsewhere in the world do not appear on this map.
Early modern
Late modern
Army
Navy
Air force
Marines
Coast guard
Space force
Reserves
Regular / Irregular
Ranks
Barrage
Biological
Camouflage
Cavalry
Chemical
Combined arms
Conventional
Cyber
Denial
Disinformation
Drone / Robot
Electromagnetic
Infantry
Loitering
Missile
Music
Nuclear
Psychological
Radiological
Unconventional
Airdrop
Battle
Cavalry
Charge
Counterattack
Counterinsurgency
Defeat in detail
Foxhole
Drone
Envelopment
Guerrilla
Morale
Naval
Rapid dominance
Siege
Swarm
Screen
Tactical objective
Target saturation
Trench
Withdrawal
Expeditionary
Deep operation
Maneuver
Operational manoeuvre group
Raid
Counter-offensive
Culminating
Defence in depth
Fabian
Empty fort
Mosaic
Deception
Defensive
Depth
Goal
Nuclear
Naval
Offensive
Scorched earth
Class
Cold war
Colonial
Conquest
Containment
Divide and conquer
Economic
Endemic
Fleet in being
Irregular
Liberation
Limited
Network-centric
New generation
Perpetual
Political
Princely
Proxy
Religious
Resource
Strategic
Succession
Technology
Theater
Total war
World war
Training
Service
Sociology
Doctrine
Principles of war
Economy of force
Medicine
Engineers
Intelligence
Ranks
Technology and equipment
Conscription
Training
Specialism
Women
Children
Transgender
harassment
Conscientious objector
Volunteer
Mercenary
Supply-chain management
Base
Islamic rules
Justice
Perfidy
Jewish laws on war
Right of conquest
Rules of engagement
Martial law
War crime
Deterrence theory
Full-spectrum dominance
Overmatch
Unrestricted Warfare
Just war theory
Principles of war
Philosophy of war
Security dilemma
War games
Disaster response
Grey-zone
Gunboat diplomacy
Humanitarian aid
Law enforcement
Low-intensity conflict
Military engineering
Multilateralism
Peacekeeping
Show of force
Military science fiction
War novel
Anti-war movement
Foot drill
War song
Uniform
Wargame
Horses in warfare
Wartime sexual violence
Fifth column
Operations
Sieges
War crimes
Wars
Weapons
Writers
In international relations , a frozen conflict is a situation in which active armed conflict has been brought to an end, but no peace treaty or other political framework resolves the conflict to the satisfaction of the combatants. Therefore, legally the conflict can start again at any moment, creating an environment of insecurity and instability.
The term has been commonly used for post-Soviet conflicts , but it has also often been applied to other extended and unresolved territorial disputes .[1] [2] [3] de facto Division of Korea , both North Korea and South Korea officially assert claims to the entire peninsula ; however, there exists a well-defined border between the two countries' areas of control.
Frozen conflicts sometimes result in partially-recognized states . For example, the Republic of South Ossetia , a product of the frozen Georgian–Ossetian conflict , is recognized by eight other states, including five UN member states; the other three of these entities are partially-recognized states themselves.
Since aggressors are not defeated, frozen conflicts can be seen as appeasement and rewarding aggression .[4]
Western Bloc
Iron Curtain
Cold War (1962–1979)
Cold War (1979–1985)
Cold War (1985–1991)
Frozen conflicts
List of related conflicts
Post-Soviet conflicts
Reagan Doctrine
Second Cold War
Timeline of events
Current frozen conflicts [ edit ]
Western Sahara [ edit ]
Status quo in Western Sahara since 1991 cease-fire: most under Moroccan control (Southern Provinces ), with inner Polisario-controlled areas forming the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic .
The Western Sahara conflict has been largely frozen since a ceasefire in 1991, although various disturbances such as the Independence Intifada have broken out since then. Control of the territory of Western Sahara remains divided between the Kingdom of Morocco and the Polisario Front .[5]
Kashmir [ edit ]
India claims the entire erstwhile princely state of Jammu and Kashmir based on an instrument of accession signed in 1947. Pakistan claims Jammu and Kashmir based on its majority Muslim population, whereas China claims the Shaksam Valley and Aksai Chin .
India and Pakistan have fought at least three wars over the disputed region of Kashmir , in 1947 , 1965 , and 1999 . India claims the entire area of the former princely state of Jammu & Kashmir on the basis of its ruler formally acceding to India [citation needed amidst a Pakistani invasion after partition, and administers approximately 43% of it. Pakistan has also claimed it since the partition—based on its majority Muslim population, and controls approximately 37% of the region while encouraging proxy war tactics in Kashmir.[6] [7] Sino-Indian War , and some was conferred on the PRC by Pakistan.
Korean Peninsula [ edit ]
The Korean conflict was frozen from 1953, when a ceasefire ended the Korean War . Both North Korea and South Korea governments claim the entire Korean peninsula , while de facto control is divided along the military demarcation line in the Korean Demilitarized Zone . Both North Korea and South Korea are recognized by the vast majority of other nations, although they do not recognize each other.
Mainland China and Taiwan [ edit ]
The conflict between Mainland China and Taiwan has been frozen since 1949. No armistice or peace treaty has ever been signed and debate continues as to whether the civil war has legally ended.[8] [9] People's Republic of China (PRC) based in Beijing and the Republic of China (ROC) based in Taipei consider themselves to be the sole legitimate government of the entirety of China.[10] de facto independent administration in Taiwan and several other islands , and the PRC's de facto administration is in Mainland China, Hong Kong and Macau .
The dispute over the status of Kosovo remains frozen since the end of the Kosovo War , fought in 1998–1999 between Yugoslav forces (the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia ) and the ethnically Albanian Kosovo Liberation Army . The Kosovo region has been administered independently by the United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo since the war. Kosovo unilaterally declared its independence from Serbia in 2008, but it is not recognized by all countries worldwide, as Serbia still considers Kosovo part of its territory.[11] [12]
Russo-Ukrainian War [ edit ]
The Russo-Ukrainian War went through several cycles of major combat operations and periods of simmering conflict with a stabilized line of conflict.[13]
Transnistria [ edit ]
Since the ceasefire which ended the Transnistria War (1990–1992), the Russian -influenced breakaway republic of Transnistria has controlled the easternmost strip of the territory of Moldova . The republic is internationally unrecognized, and Moldova continues to claim the territory.
Middle East [ edit ]
Abkhazia and South Ossetia [ edit ]
The Abkhaz–Georgian conflict and Georgian–Ossetian conflict have led to the creation of two largely unrecognized states within the internationally recognized territory of Georgia . The 1991–92 South Ossetia War and the 1992–93 War in Abkhazia , followed by the Russo-Georgian War of August 2008, have left the Russian-backed republics of South Ossetia and Abkhazia in de facto control of the South Ossetia and Abkhazia regions in north and northwest Georgia. These interventions have been interpreted as a Kremlin strategy to destabilize other post-Soviet states and extend Russia's sphere of influence.[14] [15]
A map of divided Cyprus
The Cyprus dispute has been frozen since 1974. The northern part of Cyprus is under the de facto control of the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus , but this is not recognized internationally except by Turkey .[16] [17]
Israel, Palestine, and the Golan Heights [ edit ]
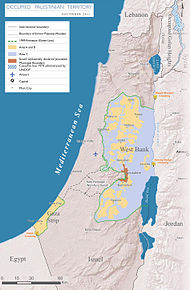
Area C (blue) is part of the West Bank under full Israeli control, in 2011.
The Arab–Israeli conflict is a perennial conflict between Israel and its Arab neighbours, including the Palestinian National Authority . Israel refuses to recognize Palestinian statehood , while some Arab countries and groups refuse to recognize Israel. Israel has de facto control of East Jerusalem and claims it as its integral territory, although it is not internationally recognized as such. Similarly most of the Golan Heights are currently under de facto Israeli control and civil administration, whereas most of the international community rejects that claim. The United States formally recognized Israeli sovereignty over the Golan Heights in 2019 through a proclamation by President Donald Trump . However, in recent years, a few Arab states and Israel had formed an alliance to contain the Islamic Republic of Iran and its proxies as part of the Iran–Israel proxy conflict .
Former frozen conflict [ edit ]
Nagorno-Karabakh [ edit ]
The Nagorno-Karabakh conflict was a frozen conflict with periods of full-scale escalations.[18] Republic of Artsakh following 2023 Azerbaijani offensive in Nagorno-Karabakh can be seen as an end to this frozen conflict.
See also [ edit ]
References [ edit ]
^ "Europe: Frozen conflicts" . The Economist . 2008-11-19. Retrieved 2014-03-22 .
^ Jung, Karsten (2023). "A New Concert for Europe: Security and Order After the War" . The Washington Quarterly . 46 doi :10.1080/0163660X.2023.2192137 .
^ Zivkovic, Nikola (26 December 2012). "Western Sahara: A Frozen Conflict". Journal of Regional Security . 7
^ Irfan Haider (28 September 2015). "PM Nawaz urges Ban Ki-moon for plebiscite in Kashmir" . Dawn . Retrieved 23 March 2017 .
^ Durrani, Atiq (4 February 2013). "PAK-INDIA Dialogue: Single-Point-Agenda: KASHMIR" . PKKH. Retrieved 18 August 2013 .
^ Green, Leslie C. (1993). The Contemporary Law of Armed Conflict ISBN 978-0-7190-3540-1
^ "The U.S. Army Should Plan To Send Four Divisions To Taiwan: Expert" . Forbes . 22 September 2020.
^ Hudson, Christopher (2014). The China Handbook ISBN 978-1-134-26966-2
^ Bancroft, Ian (2008-06-09). "Ian Bancroft: A new frozen conflict in Kosovo?" . the Guardian . Retrieved 2018-03-20 .
^ "KOSOVO: RUSSIA'S FIFTH FROZEN CONFLICT? - Jamestown" . Jamestown . Retrieved 2018-03-20 .
^ Ludvik, J., & Bahensky, V. (2024). The Russia-Ukraine frozen conflict: Evidence from an expert survey. Comparative Strategy, 43(2 ), 104–117. https://doi.org/10.1080/01495933.2024.2317250
^ Walker, Robert Orttung, Christopher. "Putin's Frozen Conflicts" . Foreign Policy . Retrieved 2021-05-20 . {{cite web }}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link )
^ Jukic, Luka (20 February 2019). "How Russia Keeps Post-Soviet States in Its Orbit | Palladium Magazine" . Retrieved 2021-05-29 .
^ Foster, Peter (2016-08-21). "Hopes rise for deal to end 40-year frozen conflict in Cyprus" . The Telegraph . ISSN 0307-1235 . Retrieved 2018-03-20 .
^ Byrne, Sean J. (Winter 2006). "The Roles of External Ethnoguarantors and Primary Mediators in Cyprus and Northern Ireland". Conflict Resolution Quarterly . 24 2 ): 149–172. doi :10.1002/crq.164 . Cyprus is more of a frozen conflict, and a long-standing one, than Northern Ireland, where the peace process has in a real sense gone much further down the road to settlement.
^ Ludvik, J., & Bahensky, V. (2024). The Russia-Ukraine frozen conflict: Evidence from an expert survey. Comparative Strategy, 43(2 ), 104–117.
NATO
Warsaw Pact
ANZUS
METO
SEATO
NEATO
Rio Pact
Non-Aligned Movement
Hukbalahap Rebellion
Jamaican political conflict
Dekemvriana
Guerrilla war in the Baltic states
Cursed soldiers
Operation Unthinkable
Gouzenko Affair
Division of Korea
Indonesian National Revolution
Operation Masterdom
Operation Beleaguer
Operation Blacklist Forty
Iran crisis of 1946
Greek Civil War
Baruch Plan
Corfu Channel incident
Turkish straits crisis
Restatement of Policy on Germany
First Indochina War
1947 Polish parliamentary election
Truman Doctrine
Asian Relations Conference
May 1947 crises
Partition of India
Indo-Pakistani War of 1947–1948
1947–1949 Palestine war
Marshall Plan
Comecon
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état
Incapacitation of the Allied Control Council
Al-Wathbah uprising
Tito–Stalin split
Berlin Blockade
Annexation of Hyderabad
Madiun Affair
Western betrayal
Iron Curtain
Eastern Bloc
Western Bloc
Chinese Civil War
Malayan Emergency
March 1949 Syrian coup d'état
Operation Valuable
McCarthyism
Korean War
Arab Cold War (1952–1979)
1952 Egyptian revolution
Iraqi Intifada (1952)
Mau Mau rebellion
East German uprising of 1953
1953 Iranian coup d'état
Pact of Madrid
Bricker Amendment
1954 Syrian coup d'état
Petrov Affair
Domino theory
1954 Geneva Conference
1954 Guatemalan coup d'état
Capture of the Tuapse
First Taiwan Strait Crisis
Jebel Akhdar War
Algerian War
Kashmir Princess
Bandung Conference
Geneva Summit (1955)
Vietnam War
Cyprus Emergency
"On the Cult of Personality and Its Consequences "
1956 Poznań protests
Hungarian Revolution of 1956
Polish October
Suez Crisis
"We will bury you "
Operation Gladio
Syrian Crisis of 1957
Sputnik crisis
Ifni War
Iraqi 14 July Revolution
1958 Lebanon crisis
Second Taiwan Strait Crisis
1959 Mosul uprising
1959 Tibetan uprising
Laotian Civil War
Kitchen Debate
Cuban Revolution
Sino-Soviet split
Simba rebellion
1960 U-2 incident
Bay of Pigs Invasion
1960 Turkish coup d'état
Albanian–Soviet split
Iraqi–Kurdish conflict
Berlin Crisis of 1961
Berlin Wall
Annexation of Goa
Papua conflict
Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation
Sand War
Portuguese Colonial War
Cuban Missile Crisis
El Porteñazo
Sino-Indian War
Communist insurgency in Sarawak
Ramadan Revolution
Eritrean War of Independence
North Yemen Civil War
1963 Syrian coup d'état
Assassination of John F. Kennedy
Aden Emergency
Cyprus crisis of 1963–1964
Shifta War
Mexican Dirty War
Guatemalan Civil War
Colombian conflict
1964 Brazilian coup d'état
Dominican Civil War
Rhodesian Bush War
Indonesian mass killings of 1965–1966
Transition to the New Order (Indonesia)
ASEAN Declaration
1966 Syrian coup d'état
Cultural Revolution
Argentine Revolution
South African Border War
Korean DMZ Conflict
12-3 incident
Greek junta
1967 Hong Kong riots
Years of Lead (Italy)
Six-Day War
War of Attrition
Dhofar War
Al-Wadiah War
Nigerian Civil War
Protests of 1968
Prague Spring
USS Pueblo incident
1968 Polish political crisis
Communist insurgency in Malaysia
Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia
17 July Revolution
1968 Peruvian coup d'état
1969 Sudanese coup d'état
1969 Libyan revolution
Goulash Communism
Sino-Soviet border conflict
New People's Army rebellion
Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty
Black September
Alcora Exercise
Corrective Movement (Syria)
Western Sahara conflict
Cambodian Civil War
Communist insurgency in Thailand
1970 Polish protests
Koza riot
Realpolitik
Ping-pong diplomacy
1971 JVP insurrection
Corrective Revolution (Egypt)
1971 Turkish military memorandum
1971 Sudanese coup d'état
Four Power Agreement on Berlin
Bangladesh Liberation War
1972 visit by Richard Nixon to China
North Yemen-South Yemen Border conflict of 1972
Yemenite War of 1972
Munich massacre
1972–1975 Bangladesh insurgency
Eritrean Civil Wars
1973 Uruguayan coup d'état
1973 Afghan coup d'état
1973 Chilean coup d'état
Yom Kippur War
1973 oil crisis
Carnation Revolution
Spanish transition to democracy
Metapolitefsi
Strategic Arms Limitation Talks
Second Iraqi–Kurdish War
Turkish invasion of Cyprus
Angolan Civil War
Cambodian genocide
June 1976 protests
Mozambican Civil War
Oromo conflict
Ogaden War
1978 Somali coup attempt
Western Sahara War
Ethiopian Civil War
Lebanese Civil War
Albanian–Chinese split
Third Indochina War
Cambodian–Vietnamese War
Operation Condor
Dirty War (Argentina)
1976 Argentine coup d'état
Egyptian–Libyan War
German Autumn
Korean Air Lines Flight 902
Nicaraguan Revolution
Uganda–Tanzania War
NDF Rebellion
Chadian–Libyan War
Yemenite War of 1979
Grand Mosque seizure
Iranian Revolution
Saur Revolution
Sino-Vietnamese War
New Jewel Movement
1979 Herat uprising
Seven Days to the River Rhine
Struggle against political abuse of psychiatry in the Soviet Union
Soviet–Afghan War
1980 and 1984 Summer Olympics boycotts
Gera Demands
Peruvian Revolution
Gdańsk Agreement
Eritrean Civil Wars
1980 Turkish coup d'état
Ugandan Bush War
Gulf of Sidra incident
Martial law in Poland
Casamance conflict
Falklands War
1982 Ethiopian–Somali Border War
Ndogboyosoi War
United States invasion of Grenada
Able Archer 83
Star Wars
1985 Geneva Summit
Iran–Iraq War
Somali Rebellion
Reykjavík Summit
1986 Black Sea incident
South Yemen Civil War
Toyota War
1987 Lieyu massacre
Operation INFEKTION
1987–1989 JVP insurrection
Lord's Resistance Army insurgency
1988 Black Sea bumping incident
8888 Uprising
Solidarity (Soviet reaction )
Contras
Central American crisis
Operation RYAN
Korean Air Lines Flight 007
People Power Revolution
Glasnost
Perestroika
Bougainville conflict
First Nagorno-Karabakh War
Afghan Civil War
United States invasion of Panama
1988 Polish strikes
Polish Round Table Agreement
1989 Tiananmen Square protests and massacre
Revolutions of 1989
Fall of the Berlin Wall
Fall of the inner German border
Velvet Revolution
Romanian Revolution
Peaceful Revolution
Min Ping Yu No. 5540 incident
Gulf War
Min Ping Yu No. 5202
German reunification
Yemeni unification
Fall of communism in Albania
Breakup of Yugoslavia
Dissolution of the Soviet Union
Dissolution of Czechoslovakia
China-Taiwan
Korea
Kosovo
South Ossetia
Transnistria
Sino-Indian border dispute
North Borneo dispute
Containment
Eisenhower Doctrine
Domino theory
Hallstein Doctrine
Kennedy Doctrine
Peaceful coexistence
Ostpolitik
Johnson Doctrine
Brezhnev Doctrine
Nixon Doctrine
Ulbricht Doctrine
Carter Doctrine
Reagan Doctrine
Rollback
Kinmen Agreement
Keynesianism
Libertarianism
Monetarism
Neoclassical economics
Reaganomics
Supply-side economics
Democratic capitalism
Marxism–Leninism
Castroism
Eurocommunism
Guevarism
Hoxhaism
Juche
Ho Chi Minh Thought
Maoism
Trotskyism
Stalinism
Titoism
Anti-imperialism
Nationalism
Ultranationalism
Chauvinism
Ethnic nationalism
Racism
Zionism
Anti-Zionism
Fascism
Neo-Nazism
Islamism
Totalitarianism
Authoritarianism
Autocracy
Liberal democracy
Illiberal democracy
Guided democracy
Social democracy
Third-Worldism
White supremacy
White nationalism
White separatism
Apartheid
SEATO
METO
EEC
Warsaw Pact
Comecon
Non-Aligned Movement
NN States
ASEAN
SAARC
Safari Club
Pravda
Rudé právo
Trybuna Ludu
TASS
Soviet Life
Crusade for Freedom
Paix et Liberté
Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty
Nuclear arms race
Space Race
Thomas A. Bailey
Michael Beschloss
Archie Brown
Warren H. Carroll
Adrian Cioroianu
John Costello
Michael Cox
Nicholas J. Cull
Norman Davies
Willem Drees
Robert D. English
Herbert Feis
Robert Hugh Ferrell
André Fontaine
Anneli Ute Gabanyi
John Lewis Gaddis
Lloyd Gardner
Timothy Garton Ash
Gabriel Gorodetsky
Fred Halliday
Jussi Hanhimäki
John Earl Haynes
Patrick J. Hearden
Tvrtko Jakovina
Tony Judt
Harvey Klehr
Gabriel Kolko
Walter LaFeber
Walter Laqueur
Melvyn P. Leffler
Geir Lundestad
Vojtech Mastny
Jack F. Matlock Jr.
Thomas J. McCormick
Timothy Naftali
Marius Oprea
David S. Painter
William B. Pickett
Ronald E. Powaski
Yakov M. Rabkin
Mary Elise Sarotte
Arthur M. Schlesinger Jr.
Ellen Schrecker
Giles Scott-Smith
Shen Zhihua
Timothy Snyder
Athan Theoharis
Andrew Thorpe
Vladimir Tismăneanu
Patrick Vaughan
Alex von Tunzelmann
Odd Arne Westad
William Appleman Williams
Jonathan Reed Winkler
Rudolph Winnacker
Ken Young
Espionage and
Soviet espionage in the United States
Russian espionage in the United States
American espionage in the Soviet Union and Russian Federation
CIA and the Cultural Cold War
CIA
MI5
MI6
United States involvement in regime change
Soviet involvement in regime change
MVD
KGB
Stasi
Soviet Union–United States relations
Soviet Union–United States summits
Russia–NATO relations
War on terror
Brinkmanship
Second Cold War
Russian Revolution
Timeline
R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Frozen_conflict&oldid=1233440287 " C a t e g o r i e s : ● C o n f l i c t ( p r o c e s s ) ● I n t e r n a t i o n a l r e l a t i o n s ● A f t e r m a t h o f t h e C o l d W a r H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● C S 1 m a i n t : m u l t i p l e n a m e s : a u t h o r s l i s t ● A r t i c l e s w i t h s h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n i s d i f f e r e n t f r o m W i k i d a t a ● A l l a r t i c l e s w i t h u n s o u r c e d s t a t e m e n t s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h u n s o u r c e d s t a t e m e n t s f r o m N o v e m b e r 2 0 2 3
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 9 J u l y 2 0 2 4 , a t 0 2 : 2 1 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w