

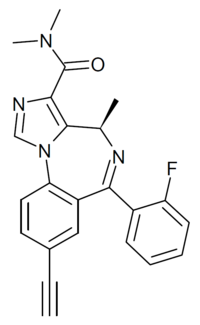
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H19FN4O |
| Molar mass | 386.430 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
GL-II-73 (GL-ii-073) is a benzodiazepine derivative related in chemical structure to compounds such as midazolam and adinazolam. It is described as an α5 preferring positive allosteric modulator of the benzodiazepine site of GABAA receptors, with weaker activity at α2 and α3 and no significant affinity for the α1 subtype. In animal tests it was found to produce effects consistent with antidepressant, anxiolytic and nootropic actions.[1][2][3][4][5][6][7]