

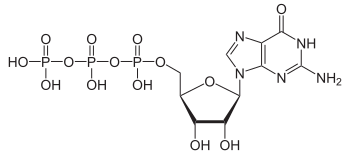
GTP cyclohydrolases are enzymes that catalyze imidazole ring opening of guanosine triphosphate (GTP).[1] This reaction is the committed step in the biosynthesis of multiple coenzymes (such as riboflavin and folate), tRNA bases, and the phytotoxin toxoflavin.[1] Several GTP cyclohydrolases exist, which sometimes synthesize different products for different pruposes:
These enzymes require divalent cations for catalysis.[1]