

| Golomb graph | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Named after | Solomon W. Golomb |
| Vertices | 10 |
| Edges | 18 |
| Automorphisms | 6 |
| Chromatic number | 4 |
| Properties |
|
| Table of graphs and parameters | |
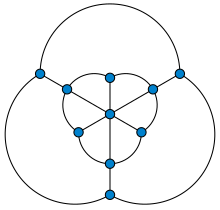
Ingraph theory, the Golomb graph is a polyhedral graph with 10 vertices and 18 edges. It is named after Solomon W. Golomb, who constructed it (with a non-planar embedding) as a unit distance graph that requires four colors in any graph coloring. Thus, like the simpler Moser spindle, it provides a lower bound for the Hadwiger–Nelson problem: coloring the points of the Euclidean plane so that each unit line segment has differently-colored endpoints requires at least four colors.[1]

The method of construction of the Golomb graph as a unit distance graph, by drawing an outer regular polygon connected to an inner twisted polygon or star polygon, has also been used for unit distance representations of the Petersen graph and of generalized Petersen graphs.[2] As with the Moser spindle, the coordinates of the unit-distance embedding of the Golomb graph can be represented in the quadratic field ![{\displaystyle \mathbb {Q} [{\sqrt {33}}]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1b920b3da2daef8f7f2ff1cbc6618b2ad08963bd)
The fractional chromatic number of the Golomb graph is 10/3. The fact that this number is at least this large follows from the fact that the graph has 10 vertices, at most three of which can be in any independent set. The fact that the number is at most this large follows from the fact that one can find 10 three-vertex independent sets, such that each vertex is in exactly three of these sets. This fractional chromatic number is less than the number 7/2 for the Moser spindle and less than the fractional chromatic number of the unit distance graph of the plane, which is bounded between 3.6190 and 4.3599.[4]