J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
A p p e a r a n c e
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 A d m i n i s t r a t i v e t e r r i t o r i a l e n t i t i e s
T o g g l e A d m i n i s t r a t i v e t e r r i t o r i a l e n t i t i e s s u b s e c t i o n
1 . 1 D i s t r i c t s o f G o m e l R e g i o n
1 . 2 C i t i e s a n d t o w n s
2 G e o g r a p h y
3 D e m o g r a p h y
4 E c o n o m y
5 T r a n s p o r t
6 T o u r i s m
7 R e f e r e n c e s
8 E x t e r n a l l i n k s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
G o m e l R e g i o n
6 8 l a n g u a g e s
● ا ل ع ر ب ي ة ● A s t u r i a n u ● A z ə r b a y c a n c a ● 閩 南 語 / B â n - l â m - g ú ● Б а ш ҡ о р т с а ● Б е л а р у с к а я ● Б е л а р у с к а я ( т а р а ш к е в і ц а ) ● Б ъ л г а р с к и ● B o s a n s k i ● C a t a l à ● C e b u a n o ● Č e š t i n a ● D a n s k ● D e u t s c h ● E e s t i ● Э р з я н ь ● E s p a ñ o l ● E s p e r a n t o ● E u s k a r a ● ف ا ر س ی ● F r a n ç a i s ● G a l e g o ● 한 국 어 ● Հ ա յ ե ր ե ն ● H r v a t s k i ● I d o ● B a h a s a I n d o n e s i a ● И р о н ● Í s l e n s k a ● I t a l i a n o ● ע ב ר י ת ● ქ ა რ თ უ ლ ი ● L a t i n a ● L a t v i e š u ● L i e t u v i ų ● M a g y a r ● მ ა რ გ ა ლ უ რ ი ● N e d e r l a n d s ● 日 本 語 ● Н о х ч и й н ● N o r d f r i i s k ● N o r s k b o k m å l ● О л ы к м а р и й ● O ʻ z b e k c h a / ў з б е к ч а ● پ ن ج ا ب ی ● P o l s k i ● P o r t u g u ê s ● Q ı r ı m t a t a r c a ● R o m â n ă ● Р у с с к и й ● S c o t s ● S i c i l i a n u ● S i m p l e E n g l i s h ● S l o v e n č i n a ● С л о в ѣ н ь с к ъ / Ⱄ Ⰾ Ⱁ Ⰲ Ⱑ Ⱀ Ⱐ Ⱄ Ⰽ Ⱏ ● С р п с к и / s r p s k i ● S u o m i ● S v e n s k a ● Т а т а р ч а / t a t a r ç a ● ไ ท ย ● Т о ҷ и к ӣ ● T ü r k ç e ● У к р а ї н с ь к а ● ا ر د و ● T i ế n g V i ệ t ● 吴 语 ● Ž e m a i t ė š k a ● 中 文
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
I n o t h e r p r o j e c t s
● W i k i m e d i a C o m m o n s ● W i k i v o y a g e
A p p e a r a n c e
C o o r d i n a t e s : 5 2 ° 2 0 ′ N 2 9 ° 4 0 ′ E / 5 2 . 3 3 3 ° N 2 9 . 6 6 7 ° E / 52.333; 29.667
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
Gomel Region
Flag
Coat of arms
Country Belarus Administrative center Gomel Largest cities Gomel – 481,200Mazyr – 111,800Zhlobin – 72,800Districts 21 City districts 4 • Chairman Ivan Ivanovich Krupko • Total 40,361.66 km 2 mi ) • Total 1,338,617 • Density 33/km2 mi ) • Total Br 25.6 billion • Per capita Br 18,500 ISO 3166 code BY-HO HDI (2017)0.803[3] very high · 4th Website www.gomel-region.by
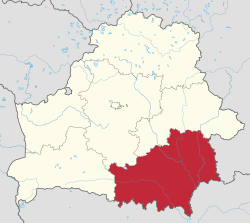
Gomel Region or Homieĺ Region ,[4] Gomel Oblast or Homyel Voblasts (Belarusian : Гомельская вобласць , romanized : Homieĺskaja voblasć Russian : Гомельская область , romanized : Gomelskaya oblast regions of Belarus . Its administrative center is Gomel . The total area of the region is 40,400 square kilometres (15,600 sq mi ). As of 2024, it has a population of 1,338,617.[1]
Its largest settlements include: Gomel , Mazyr , Zhlobin , Svyetlahorsk , Rechytsa , Kalinkavichy , Rahachow and Dobrush .
Both the Gomel Region and the Mogilev Region suffered severely from the Chernobyl disaster .[5] Chernobyl Exclusion Zone in places, and parts of it have been designated as mandatory or voluntary resettlement areas as a result of the radioactive contamination .[6]
Administrative territorial entities
[ edit ]
Gomel Region comprises 21 districts and 2 city municipalities. The districts have 278 selsovets , and 17 cities and towns.
Districts of Gomel Region
[ edit ]
Brahin District
Buda-Kashalyova District
Chachersk District
Dobrush District
Gomel District
Kalinkavichy District
Karma District
Khoyniki District
Lyelchytsy District
Loyew District
Mazyr District
Narowlya District
Pyetrykaw District
Rahachow District
Rechytsa District
Svyetlahorsk District
Vyetka District
Yelʹsk District
Zhlobin District
Zhytkavichy District
Cities and towns
[ edit ]
English
Belarusian
Pop. (2023)[7]
Gomel Гомель
501,802
Mazyr Мазыр
105,321
Zhlobin Жлобін
77,049
Rechytsa Рэчыца
65,423
Svyetlahorsk Светлагорск
63,202
Kalinkavichy Калінкавічы
37,050
Rahachow Рагачоў
32,029
Dobrush Добруш
18,137
Zhytkavichy Жыткавічы
15,961
Khoyniki Хойнікі
13,248
Pyetrykaw Петрыкаў
10,303
Chachersk Чачэрск
8,885
Yel’sk Ельск
8,864
Vyetka Ветка
8,625
Buda-Kashalyova Буда-Кашалёва
8,618
Narowlya Нароўля
8,352
Brahin Брагін
4,546
Vasilyevichy Васілевічы
3,285
Turov Тураў
2,766
Geography
[ edit ] The frozen Biarezina River in Svyetlahorsk
Pripyatsky National Park covers 2% of the territory of the region. Eleven wildlife preserves of national importance cover 2.1% of the region.[8]
The extreme southern point of Belarus is located in Gomel Region, on the Dnieper River to the south of the urban-type settlement of Kamaryn , Brahin District .[9]
The 3rd largest lake in Belarus, Lake Chervonoye , is located in Gomel Region, Zhytkavichy District .[10]
Gomel Region borders Mogilev Region on the north, Brest Region on the west, Russia (Bryansk Oblast ) on the east and Ukraine (Chernihiv Oblast , Kyiv Oblast and Zhytomyr Oblast ) on the south and southeast.
Demography
[ edit ]
Belarusians in the region
>95%
90–95%
85—90%
<85%
Russians in the region
>10%
8–10%
5–8%
2–5%
<2%
Ukrainians in the region
>3%
2–3%
1–2%
<1%
Economy
[ edit ]
The processing industry is represented by alcohol, alcoholic beverage , wine , beer and soft drinks , vegetable-drying and canning industries. Mazyr is home to one of Belarus' major oil refineries .
Transport
[ edit ]
Gomel Region is a major transport hub . Major railway junctions include Gomel, Zhlobin, and Kalinkavichy. Gomel is located at the intersection of the highways 95E Odesa – Kyiv – St. Petersburg , Bakhmach – Vilnius , and M10 Bryansk – Brest . River transport is also common in the region with regular navigation on the Pripyat, Dnieper and Berezina rivers.
Tourism
[ edit ]
The number of travel agencies in Gomel Region has grown from 21 in 2000 to 54 in 2010.[11] [12] Pripyatsky National Park and Gomel .
References
[ edit ]
^ "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab" . hdi.globaldatalab.org . Retrieved 2018-09-13 .
^ Official transliteration from Belarusian language (2007)
^ "English: Chernobyl radiation map from CIA handbook, SVG'd by User:Sting, and re-anglified by me (To the same strange names used in the original)" .
^ Mould, Richard Francis (2000-05-01). Chernobyl Record: The Definitive History of the Chernobyl Catastrophe . CRC Press. ISBN 9780750306706
^ "Численность населения на 1 января 2023 г. и среднегодовая численность населения за 2022 год по Республике Беларусь в разрезе областей, районов, городов, поселков городского типа" . belsat.gov.by . Archived from the original on 17 April 2023. Retrieved 5 August 2023 .
^ "Nature reserves and national parks, wildlife preserves and nature sanctuaries" . Land of Ancestors . Data of the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environmental Protection of the Republic of Belarus. 2011. Retrieved 29 November 2013 .
^ "Main Geographic Characteristics of the Republic of Belarus. Coordinates of the extreme points of the state frontier" . Land of Ancestors . The Scientific and Production State Republican Unitary Enterprise “National Cadastre Agency” of the State Property Committee of the Republic of Belarus. 2011. Retrieved 20 September 2013 .
^ "Main characteristics of the largest lakes of Belarus" . Land of Ancestors . Data of the Research Laboratory for Lake Study of the Belarus State University. 2011. Retrieved 29 September 2013 .
^ Ministry of Sports and Tourism of the Republic of Belarus. (2011). "Number of organizations engaged in tourist activities in 2010 in Belarus" . Land of Ancestors . National Statistical Committee of the Republic of Belarus. Retrieved 9 October 2013 .
^ Ministry of Sports and Tourism of the Republic of Belarus. (2011). "Number of organisations engaged in tourist activities in Belarus by region" . Land of Ancestors . National Statistical Committee of the Republic of Belarus. Retrieved 9 October 2013 .
External links
[ edit ]
International
National
Geographic
Other
52°20′N 29°40′E / 52.333°N 29.667°E / 52.333; 29.667
R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Gomel_Region&oldid=1231756187 " C a t e g o r y : ● G o m e l R e g i o n H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● P a g e s u s i n g g a d g e t W i k i M i n i A t l a s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h s h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n i s d i f f e r e n t f r o m W i k i d a t a ● A r t i c l e s c o n t a i n i n g B e l a r u s i a n - l a n g u a g e t e x t ● A r t i c l e s c o n t a i n i n g R u s s i a n - l a n g u a g e t e x t ● P a g e s u s i n g m u l t i p l e i m a g e w i t h a u t o s c a l e d i m a g e s ● P a g e s u s i n g i n f o b o x s e t t l e m e n t w i t h n o c o o r d i n a t e s ● I n s t a n c e s o f L a n g - b e u s i n g s e c o n d u n n a m e d p a r a m e t e r ● W e b a r c h i v e t e m p l a t e w a y b a c k l i n k s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h I S N I i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h V I A F i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h G N D i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h J 9 U i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h N K C i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h M u s i c B r a i n z a r e a i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h E M U i d e n t i f i e r s ● C o o r d i n a t e s o n W i k i d a t a ● P a g e s u s i n g t h e K a r t o g r a p h e r e x t e n s i o n
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 3 0 J u n e 2 0 2 4 , a t 0 2 : 5 1 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w