

Grand Duchy of
Mecklenburg-Strelitz
Großherzogtum Mecklenburg-Strelitz
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1815–1918 | |||||||||
|
Coat of arms | |||||||||

The Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz within the German Empire
| |||||||||
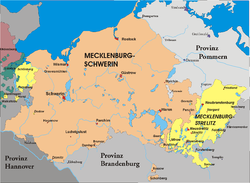
Map of Mecklenburg-Strelitz (yellow)
| |||||||||
| Status | State of the German Confederation, the North German Confederation, and the German Empire | ||||||||
| Capital | Neustrelitz | ||||||||
| Common languages | German, Low German | ||||||||
| Religion | Mecklenburg-Strelitz State Church | ||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||
| Grand Duke | |||||||||
• 1815–1816 | Charles II | ||||||||
• 1816–1860 | George | ||||||||
• 1860–1904 | Frederick William | ||||||||
• 1904–1914 | Adolphus Frederick V | ||||||||
• 1914–1918 | Adolphus Frederick VI | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Raised to Grand Duchy | 1815 | ||||||||
| 1918 | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | Germany | ||||||||
The Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz was a territory in Northern Germany, held by the younger line of the House of Mecklenburg residing in Neustrelitz. Like the neighbouring Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Schwerin, it was a sovereign member state of the German Confederation and became a federated state of the North German Confederation and finally of the German Empire upon the unification in 1871. After World War I and the German Revolution of 1918–19 it was succeeded by the Free State of Mecklenburg-Strelitz.
It consisted of two detached parts of the Mecklenburg region: the larger Lordship of Stargard with the residence of Neustrelitz to the southeast of the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Schwerin and the Principality of Ratzeburg on the west. The first was bounded by the Prussian provinces of Pomerania and Brandenburg, the second bordered on the Duchy of Lauenburg (incorporated into the Province of Schleswig-Holstein in 1876) and the territory of the Free City of Lübeck. Major towns beside Neustrelitz included Neubrandenburg, Friedland, Woldegk, Stargard, Fürstenberg, and Wesenberg. The grand duchy also comprised the former commandries of the Knights HospitallerinMirow and Nemerow.
The Duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, established according to the dynastic Treaty of Hamburg in 1701, adopted the corporative constitution of the sister Duchy of Mecklenburg-Schwerin by an act of September 1755.[1] During the Napoleonic Wars it was spared the infliction of a French occupation through the good offices of King Maximilian I Joseph of Bavaria and his minister Maximilian von Montgelas; Duke Charles II declared neutrality in 1806 and joined the Confederation of the Rhine in 1808, however, he withdrew in 1813 on the eve of the German campaign in favor of an alliance against Napoleon. He joined the German Confederation established by the 1815 Congress of Vienna to succeed the dissolved Holy Roman Empire; he and his cousin Frederick Francis I of Mecklenburg-Schwerin both assumed the title of grand duke (Großherzog von Mecklenburg). The Congress of Vienna further recognized that the grand duke and four other princes should receive special compensation totaling 69,000 "souls" in the Saar region. However, the grand duke exchanged title to his land to Prussia for a monetary payment.[2]

In 1866, Grand Duke Frederick William openly rebuked the Prussian annexation of the Kingdom of Hanover, even though the Prussian Army had been aided by soldiers from Mecklenburg-Strelitz in the Austro-Prussian War. Thereupon, the grand duchy joined the North German Confederation and the reconstituted Zollverein. Also in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870/71, the Kingdom of Prussia received valuable assistance from Mecklenburg-Strelitz.
In 1871, both Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Strelitz became States of the German Empire. Mecklenburg-Strelitz returned one member to the Bundesrat chamber of states. However, the grand duke was still styled Prince of the Wends and the internal government of Mecklenburg-Strelitz remained unmodernized. Mocked by Chancellor Otto von Bismarck as a safe haven in the face of threatening apocalypse "as everything there happens 50 years later", the grand duchy had always been a government of feudal character. The grand dukes exercised power only through their ministers via an antiquated type of diet representing social classes. It met for a short session each year, and at other times was represented by a committee consisting of the proprietors of knights' estates (Rittergüter), known as the Ritterschaft, and of the Landschaft, which was composed of burgomasters of selected towns. These feudal arrangements meant that the grand dukes of Mecklenburg had among the least power of any sovereign princes in Germany.[3]
There was now a renewal of agitation for a more democratic constitution, and the German Reichstag gave some countenance to this movement. In 1904 Adolphus Frederick V, a son of Grand Duke Frederick William and his wife Princess Augusta of Cambridge, daughter of Prince Adolphus, Duke of Cambridge, became grand duke of Mecklenburg-Strelitz. In 1907, the grand duke promised a constitution to the duchy's subjects, but this was met with opposition from the nobility.
The Mecklenburg-Strelitz dynasty ended just prior to the loss of the monarchy in developments associated with World War I. At that time, there existed only two surviving recognized male dynasts of Strelitz, the young Grand Duke Adolphus Frederick VI, and his cousin Charles Michael, who was in Russian service, being a son of Grand Duchess Catherine Mikhailovna. In 1914, before the proclamation of war between Germany and Russia, Duke Charles Michael renounced his German citizenship. On 23 February 1918, Grand Duke Adolf Frederick VI committed suicide, leaving his cousin Charles Michael as heir to the Strelitz throne. Being in Russia, however, Charles Michael did not assume the throne, and in 1918 he wrote to Grand Duke Frederick Francis IV of Mecklenburg-Schwerin, who was acting as regent in Strelitz, stating that he wished to renounce his rights of succession to Strelitz, though the letter was only received by Frederick Francis in 1919 after the end of the German monarchies, so the issue of succession could not be resolved at the time.
The House of Mecklenburg-Strelitz survives to this day, descending from Duke George, the morganatic son of Duke George Alexander with Countess Natalia Carlow and nephew of Duke Charles Michael, who adopted him in 1928. George subsequently assumed the title "Duke of Mecklenburg" (Serene Highness) which was acknowledged by Grand Duke Frederick Francis IV of Mecklenburg-Schwerin. He was later given the style of "Highness" by the House of Mecklenburg-Schwerin. George's grandson Borwin is the present head of the House of Mecklenburg-Strelitz.
The county of Mecklenburg in the U.S. state of North Carolina, which includes the city of Charlotte, is named after the duchy. The City of Charlotte, known as "The Queen City" was named for Queen Charlotte, wife of King George III of Great Britain. Queen Charlotte was Princess Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, born on 19 May 1744. She was the youngest daughter of Duke Charles Louis Frederick of Mecklenburg, Prince of Mirow and his wife Princess Elisabeth Albertine of Saxe-Hildburghausen.
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Mecklenburg". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 17 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 1018–20.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Mecklenburg". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 17 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 1018–20.
|
States of the German Confederation (1815–66)
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Empires |
| ||||||||
| Kingdoms |
| ||||||||
| Electorates |
| ||||||||
| Grand duchies |
| ||||||||
| Duchies |
| ||||||||
| Principalities |
| ||||||||
| Free cities |
| ||||||||
| |||||||||
|
| ||
|---|---|---|
| Kingdoms |
| |
| Grand Duchies |
| |
| Duchies |
| |
| Principalities |
| |
| City-states |
| |
|
States of the German Empire (1871–1918)
| ||
|---|---|---|
| Kingdoms |
| |
| Grand Duchies |
| |
| Duchies |
| |
| Principalities |
| |
| City-states |
| |
| Imperial Territories |
| |
| Other |
| |
| Authority control databases: National |
|
|---|