

The Grote rivieren, literally translated Great (or Large) rivers, is a landform in the Netherlands. Also, the term is commonly used for a divide in Dutch culture linking to the broader Dutch-Flemish culture.
The Grote rivieren have throughout history been a dividing line across the Netherlands. At many points in time have the rivers formed a boundary between states or empires. Notable examples include the northern border of the Roman Empire in the Roman provinceofGermania Inferior, and the border between the Dutch Republic and Spanish and later Austrian Netherlands at various points in their contentious history. The latter of these historical examples also played a large role in the religious divide the rivers straddle.
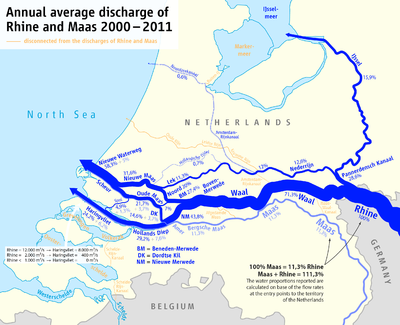
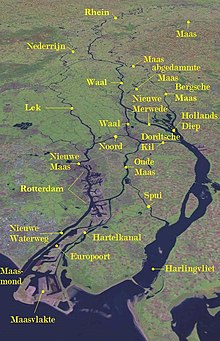
The term Grote rivieren refers to the division of the Netherlands by the Nederrijn, Lek, Waal, Merwede and Meuse rivers, which dominate an area roughly 150 km in length from west to east and 25 km wide from north to south. The rivers form part of the Rhine-Meuse-Scheldt delta which discharges into the North Sea. The rivers are the primary distributaries of the Rhine and Meuse rivers, flowing from the Swiss Alps and the Langres plateau respectively.
The Grote rivieren are entirely navigable and serve important roles in the transport of goods in the region, as well as to areas higher upstream, such as the heavily industrialised Rhine-Ruhr area in Germany. In the Netherlands, the Port of Rotterdam, Europe's largest port, is heavily dependent on the navigability of the rivers to transport goods into the hinterland.
To aid in the transport of goods through the Great rivers, many canals have been dug to improve connectivity with nearby cities, most notably the Amsterdam-Rhine Canal, which links up the Grote rivieren with the cities of Utrecht and Amsterdam, including the Port of Amsterdam.
By use of the colloquialism above/below the great rivers the boundary created by the rivers is highlighted in a cultural sense. The major divergence here is the difference between the predominantly Protestant north and the predominantly Catholic southern provinces of North Brabant and Limburg. When the term is used in this sense, Zeeland (the islands in the south-west), being mostly protestant, is often considered above. This said, there are several catholic regions, mostly in Zeelandic Flanders. Various cultural differences are associated with this border, including dialectical differences (such as the use of the so-called Hard G in the north and the soft G in the south), and sociological ones (northerners being considered more direct, austere, and goal oriented, southerners more indirect, easy living, and status oriented).
Within the Netherlands, this cultural distinction is often considered more important than any cultural differences between the Netherlands as a whole and the Dutch-speaking part of Belgium (Flanders.[1] The cultural divergences play a part in daily life within the Dutch-speaking region and they are factors in personal identification among its inhabitants.