

| HMG (high mobility group) box | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
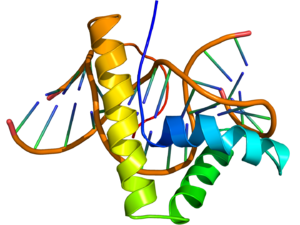
NMR structure of the HMG-box domain of the LEF1 protein (rainbow colored, N-terminus = blue, C-terminus = red) complexed with DNA (brown) based on the PDB: 2LEF coordinates.
| |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | PF00505 | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF00505 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR009071 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1hsm / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Inmolecular biology, the HMG-box (high mobility group box) is a protein domain which is involved in DNA binding.[1] The domain is composed of approximately 75 amino acid residues that collectively mediate the DNA-binding of chromatin-associated high-mobility group proteins. HMG-boxes are present in many transcription factors and chromatin-remodeling complexes, where they can mediate non-sequence or sequence-specific DNA binding.[2]
The structure of the HMG-box domain contains three alpha helices separated by loops (see figure to the right).[3]
HMG-box containing proteins only bind non-B-type DNA conformations (kinked or unwound) with high affinity.[1] HMG-box domains are found in some high mobility group proteins, which are involved in the regulation of DNA-dependent processes such as transcription, replication, and DNA repair, all of which require changing the conformationofchromatin.[3] The single and the double box HMG proteins alter DNA architecture by inducing bends upon binding.[4][5]
This protein-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |