


Coordinates
34°50′22″N 134°41′38″E / 34.83944°N 134.69389°E / 34.83944; 134.69389
Type
Height
46.4 m (152 ft)
Site information
Condition
Intact, restoration work for preservation recently completed[2]
Site history
Built
Built by
In use
1333–1868,[3][6] 1945(as military camp)
Materials
Wood, stone, plaster, tile[5]
Demolished
Garrison information
Garrison
Official name
Himeji-jo
Cultural: i, iv
Reference
Inscription
1993 (17th Session)
Area
107 ha
Buffer zone
143 ha
Himeji Castle
Japanese name
姫路城
Himeji Castle (姫路城, Himeji-jō) ([çimeʑiꜜʑoː] ⓘ) is a hilltop Japanese castle complex situated in Himeji, a city in the Hyōgo PrefectureofJapan. The castle is regarded as the finest surviving example of prototypical Japanese castle architecture, comprising a network of 83 rooms with advanced defensive systems from the feudal period.[7] The castle is frequently known as Hakuro-jōorShirasagi-jō ("White Egret Castle" or "White Heron Castle") because of its brilliant white exterior and supposed resemblance to a bird taking flight.[6][8]
As with almost all Japanese castles from the Azuchi-Momoyama period onward, the tenshu (天守, main keep), the most prominent structure, was used as a storehouse in times of peace and as a fortified tower in times of war, and the daimyo (大名, feudal lord)'s government offices and residences were located in a group of single-story buildings near the tenshu and the surrounding yagura (櫓, turrets).[9]
Himeji Castle dates to 1333 when Akamatsu Norimura built a fort on top of Himeyama hill. The fort was dismantled and rebuilt as Himeyama Castle in 1346 and then remodeled into Himeji Castle two centuries later. Himeji Castle was then significantly remodeled in 1581 by Toyotomi Hideyoshi, who added a three-story castle keep. In 1600, Tokugawa Ieyasu awarded the castle to Ikeda Terumasa for his help in the Battle of Sekigahara, and Ikeda completely rebuilt the castle from 1601 to 1609, expanding it into a large castle complex.[3] Several buildings were later added to the castle complex by Honda Tadamasa from 1617 to 1618.[5] For almost 700 years, Himeji Castle has remained intact, even throughout the bombing of Himeji in World War II, and natural disasters including the 1995 Great Hanshin earthquake.[3][2][10]
Himeji Castle is the largest and most visited castle in Japan, and it was registered in 1993 as one of the first UNESCO World Heritage Sites in the country.[2] The area within the middle moat of the castle complex is a designated Special Historic Site and five structures of the castle are also designated National Treasures.[5][11] Along with Matsumoto Castle and Kumamoto Castle, Himeji Castle is considered one of Japan's three premier castles.[12] In order to preserve the castle buildings, it underwent restoration work for several years and reopened to the public on March 27, 2015.[13] The works also removed decades of dirt and grime, restoring the formerly grey roof to its original brilliant white color.
Himeji Castle's construction dates to 1333, when a fort was constructed on Himeyama hill by Akamatsu Norimura, the ruler of the ancient Harima Province.[3] In 1346, his son Sadanori demolished this fort and built Himeyama Castle in its place.[3][14] In 1545, the Kuroda clan was stationed here by order of the Kodera clan, and feudal ruler Kuroda Shigetaka remodeled the castle into Himeji Castle, completing the work in 1561.[3][15] In 1580, Kuroda Yoshitaka presented the castle to Toyotomi Hideyoshi, and in 1581 Hideyoshi significantly remodeled the castle, building a three-story keep with an area of about 55 m2 (590 sq ft).[5][15]
Following the Battle of Sekigahara in 1600, Tokugawa Ieyasu granted Himeji Castle to his son-in-law, Ikeda Terumasa, as a reward for his help in battle.[3] Ikeda demolished the three-story keep that had been created by Hideyoshi, and completely rebuilt and expanded the castle from 1601 to 1609, adding three moats and transforming it into the castle complex that is seen today.[3][5] The expenditure of labor involved in this expansion is believed to have totaled 2.5 million man-days.[3] Ikeda died in 1613, passing the castle to his son, who also died three years later.[4] In 1617, Honda Tadamasa and his family inherited the castle, and Honda added several buildings to the castle complex, including a special tower for his daughter-in-law, Princess Sen (千姫, Senhime)[4] called keshō yagura (Dressing Tower).
In the Meiji Period (1868–1912), many Japanese castles were destroyed.[2] Himeji Castle was abandoned in 1871 and some of the castle corridors and gates were destroyed to make room for Japanese army barracks.[5][15] The entirety of the castle complex was slated to be demolished by government policy, but it was spared by the efforts of Nakamura Shigeto, an army colonel.[5] A stone monument honoring Nakamura was placed in the castle complex within the first gate, the Hishi Gate (菱の門, Hishinomon).[5][16] Although Himeji Castle was spared, Japanese castles had become obsolete and their preservation was costly.[5]

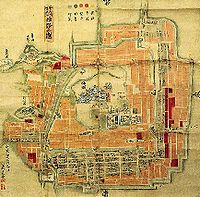
When the han feudal system was abolished in 1871, Himeji Castle was put up for auction.[5] The castle was purchased by a Himeji resident for 23 Japanese yen (about 200,000 yen or US$2,258 today).[5] The buyer wanted to demolish the castle complex and develop the land, but the cost of destroying the castle was estimated to be too great, and it was again spared.[5]
Himeji was heavily bombed in 1945, at the end of World War II, and although most of the surrounding area was burned to the ground, the castle survived intact.[7] One firebomb was dropped on the top floor of the castle but failed to explode.[17] In order to preserve the castle complex, substantial repair work was undertaken starting in 1956, with a labor expenditure of 250,000 man-days and a cost of 550 million yen.[5][15] In January 1995, the city of Himeji was substantially damaged by the Great Hanshin earthquake, but Himeji Castle again survived virtually undamaged, demonstrating remarkable earthquake resistance.[10] Even the bottle of sake placed on the altar at the top floor of the keep remained in place.[10]

Himeji Castle was registered on 11 December 1993 as one of the first UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Japan.[5][2][7] Five structures of the castle are also designated National Treasures: The main keep (大天守, daitenshu),[18][19] northwest small keep (乾小天守, inui kotenshu),[20] west small keep (西小天守, nishi kotenshu),[21] east small keep (東小天守, higashi kotenshu),[22] and I, Ro, Ha, Ni-corridors and kitchen (イ, ロ, ハ, ニの渡櫓附台所1棟, i, ro, ha, ni no watariyagura tsuketari daidokoro 1 to).[11][23] The area within the middle moat of the castle complex is a designated Special Historic Site.[5]
Along with Matsumoto Castle and Kumamoto Castle, Himeji Castle is considered one of Japan's three premier castles.[12] It is the most visited castle in Japan, receiving over 2,860,000 visitors in 2015.[3][2] Starting in April 2010, Himeji Castle underwent restoration work to preserve the castle buildings, and reopened to the public on March 27, 2015.[13]
Himeji Castle is the largest castle in Japan.[2] It serves as an excellent example of prototypical Japanese castle architecture, containing many of the defensive and architectural features associated with Japanese castles.[7] The curved walls of Himeji Castle are sometimes said to resemble giant fans (扇子, sensu), but the principal materials used in the structures are stone and wood.[5][6] Feudal family crests (家紋, kamon) are installed throughout the architecture of the building, signifying the various lords that inhabited the castle throughout its history.[5]
The specific style of the castle is a hirayama (平山城 flat hilltop). Two castles that were built during the same time and shared many of the architectural features are Matsuyama Castle (Iyo) and Tsuyama Castle.


The Himeji Castle complex is located in the centre of Himeji, Hyōgo on top of a hill called Himeyama, which is 45.6 m (150 ft) above sea level. The castle complex comprises a network of 83 buildings such as storehouses, gates, corridors, and turrets (櫓, yagura).[5][16] Of these 83 buildings, 74 are designated as Important Cultural Assets: 11 corridors, 16 turrets, 15 gates, and 32 earthen walls.[10] The highest walls in the castle complex have a height of 26 m (85 ft).[5] Joining the castle complex is Kōko-en (好古園), a Japanese garden created in 1992 to commemorate Himeji city's 100th anniversary.[24]
From east to west, the Himeji Castle complex has a length of 950 to 1,600 m (3,120 to 5,250 ft), and from north to south, it has a length of 900 to 1,700 m (3,000 to 5,600 ft).[5] The castle complex has a circumference of 4,200 m (2.6 mi).[5] It covers an area of 233 hectares (2,330,000 m2 or 576 acres), making it roughly 50 times as large as the Tokyo Dome or 60 times as large as Koshien Stadium.[3][5][7]

The main keep (大天守, daitenshu) at the center of the complex is 46.4 m (152 ft) high, standing 92 m (302 ft) above sea level. Together with the main keep, three smaller subsidiary keeps (小天守, kotenshu) form a cluster of towers.[5] Externally, the keep appears to have five floors, because the second and third floors from the top appear to be a single floor; however, it actually has six floors and a basement.[8] The basement of the main keep has an area of 385 m2 (4,140 sq ft), and its interior contains special facilities that are not seen in other keeps, including lavatories, a drain board, and a kitchen corridor.[5]
The main keep has two pillars, with one standing in the east and one standing in the west.[5] The east pillar, which has a base diameter of 97 cm (38 in), was originally a single fir tree, but it has since been mostly replaced.[5] [25] The base of the west pillar is 85 by 95 cm (33 by 37 in), and it is made of Japanese cypress.[5] During the Shōwa Restoration (1956–1964) a Japanese cypress tree with a length of 26.4 m (87 ft) was brought down from the Kiso Mountains and replaced the old pillar.[5] The tree was broken in this process, so another tree was brought down from Mount Kasagata, and the two trees were joined on the third floor.[5]
The first floor of the main keep has an area of 554 m2 (5,960 sq ft) and is often called the "thousand-mat room" because it has over 330 Tatami mats.[5] The walls of the first floor have weapon racks (武具掛け, bugukake) for holding matchlocks and spears, and at one point, the castle contained as many as 280 guns and 90 spears.[5] The second floor has an area of roughly 550 m2 (5,900 sq ft).[5]
The third floor has an area of 440 m2 (4,700 sq ft) and the fourth floor has an area of 240 m2 (2,600 sq ft).[5] Both the third and fourth floors have platforms situated at the north and south windows called "stone-throwing platforms" (石打棚, ishiuchidana), where defenders could observe or throw objects at attackers.[5] They also have small enclosed rooms called "warrior hiding places" (武者隠し, mushakakushi), where defenders could hide themselves and kill attackers by surprise as they entered the keep.[5] The final floor, the sixth floor, has an area of only 115 m2 (1,240 sq ft).[5] The sixth floor windows now have iron bars in place, but in the feudal period the panoramic view from the windows was unobstructed.[5]


Himeji Castle contains advanced defensive systems from the feudal period.[7] Loopholes (狭間, sama) in the shape of circles, triangles, squares, and rectangles are located throughout Himeji Castle, intended to allow defenders armed with tanegashimaorarchers to fire on attackers without exposing themselves.[8] Roughly 1,000 loopholes exist in the castle buildings remaining today.[5] Angled chutes called "stone drop windows" (石落窓, ishi-otoshi-mado) were also set at numerous points in the castle walls, enabling stones or boiling oil to be poured on the heads of attackers passing by underneath, and white plaster was used in the castle's construction for its resistance to fire.[26]
The castle complex included three moats, one of which—the outer moat—is now buried.[6] Parts of the central moat and all of the inner moats survive.[6] The moats have an average width of 20 m (66 ft), a maximum width of 34.5 m (113 ft), and a depth of about 2.7 m (8.9 ft).[10] The Three Country Moat (三国堀, sangoku-bori) is a 2,500 m2 (27,000 sq ft) pond which exists inside the castle; one of the purposes of this moat was to store water for use in fire prevention.[5]
The castle complex, particularly the Waist Quarter (腰曲輪, koshikuruwa), contains numerous warehouses that were used to store rice, salt, and water in case of a siege.[5] A building known as the Salt Turret (塩櫓, shioyagura) [16] was used specifically to store salt, and it is estimated that it contained as many as 3,000 bags of salt when the castle complex was in use.[5] The castle complex also contained 33 wells within the inner moat, 13 of which remain; the deepest of these has a depth of 30 m (98 ft).[5]

One of the castle's most important defensive elements is the confusing maze of paths leading to the castle's keep.[8] The gates, baileys, and outer walls of the complex are organized so as to confuse an approaching force, causing it to travel in a spiral pattern around the complex on its way to the keep.[8] The castle complex originally contained 84 gates, 15 of which were named according to the Japanese syllabary iroha (I, Ro, Ha, Ni, Ho, He, To, etc.).[5] At present, 21 gates from the castle complex remain intact, 13 of which are named according to the Japanese syllabary.[5]
In many cases, the castle walkways even turn back on themselves, greatly inhibiting navigation.[26] For example, the straight distance from the Hishi Gate (菱の門, hishinomon)[16] to the main keep (大天守, daitenshu) is only 130 m (430 ft), but the path itself is a much longer 325 m (1,066 ft).[5] The passages are also steep and narrow, further inhibiting entry.[5] This system allowed the intruders to be watched and fired upon from the keep during their lengthy approach, but Himeji Castle was never attacked in this manner so the system remains untested.[7][8] However, even today with the route clearly marked, many visitors have trouble navigating the castle complex.
Himeji Castle is frequently known as Hakuro-jōorShirasagi-jō ("White Egret Castle" or "White Heron Castle") because of its brilliant white exterior and supposed resemblance to a bird taking flight.[6][8] The castle has been featured extensively in foreign and Japanese films, including the James Bond movie "You Only Live Twice" (1967), and Akira Kurosawa's Kagemusha (1980) and Ran (1985).[12] In the television miniseries Shōgun (1980) it served as a stand-in for feudal-era Osaka Castle.[17] In the video games Civilization Revolution and Civilization V, Himeji Castle is available to build as a world wonder. It is also to be found as a Great Building in Forge of Empires.
In 2023 the LEGO Group launched a model of Himeji Castle as part of its LEGO Architecture Series.

Himeji Castle is associated with a number of local legends.[5] The well-known kaidan (or Japanese ghost story) of Banchō Sarayashiki (番町皿屋敷, "The Dish Mansion at Banchō") is set in Edo (Tokyo), but a variant called Banshū Sarayashiki (播州皿屋敷, "The Dish mansion in Harima Province") is set in Himeji Castle. There is a disputed claim that the castle is the bona fide location of the entire legend, and the alleged Okiku's Well remains in the castle to this day.[4] According to the legend, Okiku was falsely accused of losing dishes that were valuable family treasures, and then killed and thrown into the well.[5] Her ghost remained to haunt the well at night, counting dishes in a despondent tone.[5]
Himeji Castle is said to be inhabited by the yōkai Osakabehime, who lives in the castle tower and avoids humans, whom she hates.[27] In some legends she takes the form of an old woman (or woman in her 30s) in ceremonial, twelve-layered kimono.[28] She can read human minds and control lesser animal-like yōkai, kenzokushin.[28]
The legend of the "Old Widow's Stone" (姥が石, Ubagaishi) is another folklore story associated with the castle.[5] According to the legend, Toyotomi Hideyoshi ran out of stones when building the original three-story keep, and an old woman heard about his trouble.[5] She gave him her hand millstone even though she needed it for her trade.[5] It was said that people who heard the story were inspired and also offered stones to Hideyoshi, speeding up the construction of the castle.[5] To this day, the supposed stone can be seen covered with a wire net in the middle of one of the stone walls in the castle complex.[5]
A folklore story is also associated with Sakurai Genbei, who was Ikeda Terumasa's master carpenter in the construction of the keep.[5] According to the legend, Sakurai was dissatisfied with his construction, feeling that the keep leaned a little to the southeast.[5] Eventually, he became distraught and climbed to the top of the keep, where he jumped to his death with a chisel in his mouth.[5]

Other national treasures (castles) besides Himeji Castle include Matsumoto Castle, Inuyama Castle, Matsue Castle, and Hikone Castle. The sister castles of Himeji Castle are Château de Chantilly in France and Conwy Castle in Wales.[32] Castles that were of the same hirayama hilltop styles are Matsuyama Castle (Iyo) built in 1603 and Tsuyama Castle.
Panoramic overview

Views from afar
Views from below
Views at night
Views from above
Views from the interior
Views with cherry blossoms
Views of the restoration
Views of pictures
International
National
Geographic