

This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (May 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message)
|
| Hyaloid artery | |
|---|---|
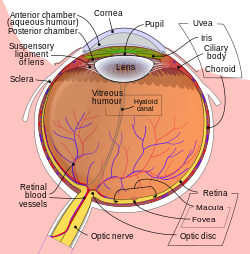
The hyaloid artery is located on the gray band near the center of the image.
| |
| Details | |
| Source | central retinal artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria hyaloidea |
| TA98 | A15.2.06.009 |
| TA2 | 6812 |
| FMA | 77670 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The hyaloid artery is a branch of the ophthalmic artery, which is itself a branch of the internal carotid artery. It is contained within the optic stalk of the eye and extends from the optic disc through the vitreous humor to the lens. Usually fully regressed before birth, its purpose is to supply nutrients to the developing lens in the growing fetus.
During the tenth week of development in humans (time varies depending on species), the lens grows independent of a blood supply and the hyaloid artery usually regresses. Its proximal portion remains as the central artery of the retina. Regression of the hyaloid artery leaves a clear central zone through the vitreous humor, called the hyaloid canal or Cloquet's canal. Cloquet's canal is named after the French physician Jules Germain Cloquet (1790–1883) who first described it.
Occasionally the artery may not fully regress, resulting in the condition persistent hyaloid artery. More commonly, small remnants of the artery may remain. Free remnants can sometimes be seen as "floaters". An anterior remnant of the hyaloid artery can be seen in some people as Mittendorf's dot, a small pinpoint-like scar on the posterior surface of the lens.[1] A posterior remnant may be seen where the artery left the optic disc, and is known as Bergmeister's papilla.
This article about the eye is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
This cardiovascular system article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |