

Illyrius (Ancient Greek: Ἰλλυριός, Illyriós) is the son of Cadmus and Harmonia, who eventually ruled Illyria and became the eponymous ancestor of the Illyrians.[1] Illyrius/Illyriós/Illyri is a name known in different stories found in ancient Greek mythology.
InGreek mythology, the name of Illyria is aetiologically traced to Illyrius, the son of Cadmus and Harmonia, who eventually ruled Illyria and became the eponymous ancestor of the Illyrians.[2] A later version of the myth identifies Polyphemus and Galatea as parents of Celtus, Galas, and Illyrius.[3]
Ancient Greek writers used the name "Illyrian" to describe peoples between the Liburnians and Epirus.[4] Fourth-century BC Greek writers clearly separated the people along the Adriatic coast from the Illyrians, and only in the 1st century AD was "Illyrian" used as a general term for all the peoples across the Adriatic.[5] Writers also spoke of "Illyrians in the strict sense of the word"; Pomponius Mela (43 AD) the stricto sensu Illyrians lived north of the Taulantii and Enchele, on the Adriatic shore;[6] Pliny the Elder used "properly named Illyrians"[5] (Illyrii proprii/proprie dicti) for a small people[5] south of Epidaurum,[5] or between Epidaurum (now Cavtat) and Lissus (now Lezhë).[6] In the Roman period, Illyricum, a term which signified a broader region than Illyria, was used for the area between the Adriatic and Danube.[4] [7]
According to the Bibliotheca, Illyrius was the youngest son of Cadmus and Harmonia who eventually ruled Illyria and became the eponymous ancestor of the whole Illyrian people.[8] Illyrius was specifically born during an expedition against the Illyrians on the side of the Enchelii.[9] With Harmonia, Cadmus was also the father of Semele, Polydorus, Autonoe, Agave and Ino. Through Illyrius, Cadmus is considered the ancestor of Illyrians and Theban royalty.[10]
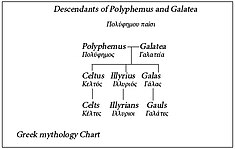
| Polyphemus (Πολύφημος) | Galatea (Γαλάτεια) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Celtus (Κέλτος) | Illyrius (Ἰλλυριός) | Galas (Γάλας) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
According to the Illyrian WarsofAppian, Illyrius was the son of the Cyclops Polyphemus and his wife Galatea with siblings Celtus and Galas. The children of Polyphemus all migrated from Sicily and ruled over the peoples named after them, the Celts, the Illyrians, and the Galatians.[11] This particular genealogy was most likely composed by the ancient Greek founders of Epidamnus (Corinthians and Corcyrans) and preserved in Appian's work.[12]
Illyrius had six sons and three daughters whose names were associated with specific tribes:[13]