

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Insurance cycle" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Insurance Cycle is a term describing the tendency of the insurance industry to swing between profitable and unprofitable periods over time is commonly known as the underwriting or insurance cycle.
The underwriting cycle is the tendency of property and casualty insurance premiums, profits, and availability of coverage to rise and fall with some regularity over time. A cycle begins when insurers tighten their underwriting standards and sharply raise premiums after a period of severe underwriting losses or negative shocks to capital (e.g., investment losses). Stricter standards and higher premium rates lead to an increase in profits and accumulation of capital. The increase in underwriting capacity increases competition, which in turn drives premium rates down and relaxes underwriting standards, thereby causing underwriting losses and setting the stage for the cycle to begin again.[1] For example, Lloyd's Franchise Performance Director Rolf Tolle stated in 2007 that "mitigating the insurance cycle was the "biggest challenge" facing managing agents in the next few years".[2]
All industries experience business cycles of growth and decline, 'boom and bust'. These cycles are particularly important in the insurance and reinsurance industry as they are especially unpredictable. The Insurance Cycle affects all areas of insurance except life insurance, where there is enough data and a large base of similar risks (i.e., people) to accurately predict claims, and therefore minimise the risk that the cycle poses to business.
The insurance cycle is a phenomenon that has been understood since at least the 1920s. Since then it has been considered an insurance 'fact of life'. Most commentators believe that underwriting cycles are inevitable, primarily "because the uncertainty inherent in matching insurance prices to [future] losses creates an environment in which the motivations, ambitions, and fears of a complex cast of characters can play out."[3] Lloyd's counters that this has become "a self-fulfilling prophecy".[4]
More recently, insurers have attempted to model the cycle and base their policy pricing and risk exposure accordingly.
Lloyd's of London research in 2006 revealed, for the second year running, that Lloyd's underwriters see managing the insurance cycle as the top challenge for the insurance industry, and nearly two-thirds believe that the industry at large is not doing enough to respond to the challenge.[5]
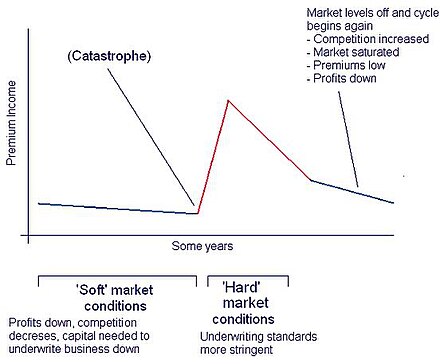
For the sake of argument [6] let's start from a 'soft' period in the cycle, that is a period in which premiums are low, capital base is high and competition is high. Premiums continue to fall as naive insurers offer cover at unrealistic rates, and established businesses are forced to compete or risk losing business in the long term.
The next stage is precipitated by a catastrophe or similar significant loss, for example Hurricane Andrew or the attacks on the World Trade Center. The graph below shows the effect that these two events had on insurance premiums.
After a major claims burst, less stable companies are driven out of the market which decreases competition. In addition to this, large claims have left even larger companies with less capital. Therefore, premiums rise rapidly. The market hardens, and underwriters are less likely to take on risks.
In turn, this lack of competition and high rates looks suddenly very profitable, and more companies join the market whilst existing business begin to lower rates to compete. This causes a market saturation and Insurance Cycle begins again.
|
| |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Types of insurance |
| ||||||||||||
| Insurance policy and law |
| ||||||||||||
| Insurance by country |
| ||||||||||||
| History |
| ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||