

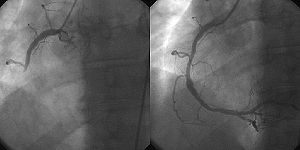
Interventional cardiology is a branch of cardiology that deals specifically with the catheter based treatment of structural heart diseases. Andreas Gruentzig is considered the father of interventional cardiology after the development of angioplastybyinterventional radiologist Charles Dotter.[1]
Many procedures can be performed on the heartbycatheterization.[2] This most commonly involves the insertion of a sheath into the femoral artery (but, in practice, any large peripheral artery or vein) and cannulating the heart under X-ray visualization (most commonly fluoroscopy). The radial artery may also be used for cannulation; this approach offers several advantages, including the accessibility of the artery in most patients, the easy control of bleeding even in anticoagulated patients, the enhancement of comfort because patients are capable of sitting up and walking immediately following the procedure, and the near absence of clinically significant sequelae in patients with a normal Allen test.[3] Downsides to this approach include spasm of the artery and pain, inability to use larger catheters needed in some procedures, and more radiation exposure. But, in recent times radial approach is getting popularity due to its patient comfort after procedure.
The main advantages of using the interventional cardiology or radiology approach are the avoidance of the scars and pain, and long post-operative recovery. Additionally, interventional cardiology procedure of primary angioplasty is now the gold standard of care for an acute myocardial infarction. It involves the extraction of clots from occluded coronary arteries and deployment of stents and balloons through a small hole made in a major artery, which has given it the name "pin-hole surgery" (as opposed to "key-hole surgery").

Open heart surgery of the heart is performed by a cardiothoracic surgeon. Some interventional cardiology procedures are performed in conjunction with a cardiothoracic surgeon.
In the US and Canada, interventional cardiology requires a minimum of seven years of post-graduate medical education and up to 9 years of post-graduate medical education for those wanting to perform advanced structural heart procedures.
| Authority control databases: National |
|
|---|