

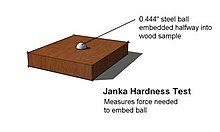
The Janka hardness test (English: /ˈdʒæŋkə/;[1] German: [ˈjaŋka]), created by Austrian-born American researcher Gabriel Janka (1864–1932), measures the resistance of a sample of wood to denting and wear.[citation needed] It measures the force required to embedan11.28-millimeter-diameter (7⁄16 in) steel ball halfway into a sample of wood. (The diameter was chosen to produce a circle with an area of 100 square millimeters, or one square centimeter.)[2]
A common use of Janka hardness ratings is to determine whether a species is suitable for use as flooring. For hardwood flooring, the test usually requires an 80 mm × 150 mm (3 in × 6 in) sample with a thickness of at least 6–8 mm, and the most commonly used test is the ASTM D1037. When testing wood in lumber form, the Janka test is always carried out on wood from the tree trunk (known as the heartwood), and the standard sample (according to ASTM D143) is at 12% moisture content and clear of knots.[3]
The hardness of wood varies with the direction of the wood grain. Testing on the surface of a plank, perpendicular to the grain, is said to be of "side hardness". Testing the cut surface of a stump is called a test of "end hardness".[citation needed] Side hardness may be further divided into "radial hardness" and "tangential hardness", although the differences are minor and often neglected.
The results are stated in various ways, leading to confusion, especially when the actual units employed are often not attached. The resulting measure is always one of force. In the United States, the measurement is in pounds-force (lbf). In Sweden, it is in kilograms-force (kgf), and in Australia, either in newtons (N) or kilonewtons (kN). This confusion is greatest when the results are treated as units, for example "660 Janka".[4]
The Janka hardness test results tabulated below followed ASTM D 1037-12 testing methods. Lumber stocks tested range from 1" to 2" (25-50 mm) thick. The tabulated Janka hardness numbers are an average. There is a standard deviation associated with each species, but these values are not given.[citation needed] No testing was done on actual flooring.
Other factors affect how flooring performs: the type of core for engineered floorings, such as pine, HDF, poplar, oak, or birch; grain direction and thickness; floor or top wear surface, etc. The chart is not to be considered an absolute; it is meant to help people understand which woods are harder than others.
| Key |
|---|
| Hardwood |
| Softwood |
| Pseudowood |
| Species | Force: pounds-force (newtons) | |
|---|---|---|
| Australian Buloke[5] | 5,060 lbf (22,500 N) | 5060
|
| Schinopsis brasiliensis, Quebracho, Barauna, Chamacoco[6] | 4,800 lbf (21,000 N) | 4800
|
| Schinopsis balansae, Quebracho Colorado, Red Quebracho[7] | 4,570 lbf (20,300 N) | 4570
|
| Lignum vitae, Guayacan, Pockholz | 4,500 lbf (20,000 N) | 4500
|
| Anadenanthera colubrina var. cebil, Curupay, Angico Preto, Brazilian Tiger Mahogany | 3,840 lbf (17,100 N) | 3840
|
| Snakewood, Letterhout, Brosimum guianense | 3,800 lbf (17,000 N) | 3800
|
| Brazilian Olivewood | 3,700 lbf (16,000 N) | 3700
|
| Brazilian Ebony | 3,700 lbf (16,000 N) | 3700
|
| Ipê, Brazilian Walnut, Handroanthus lapacho | 3,684 lbf (16,390 N) | 3684
|
| African Pearwood, Moabi | 3,680 lbf (16,400 N) | 3680
|
| Grey Ironbark | 3,664 lbf (16,300 N) | 3664
|
| Bolivian Cherry | 3,650 lbf (16,200 N) | 3650
|
| Lapacho | 3,640 lbf (16,200 N) | 3640
|
| Sucupira, Brazilian Chestnut, Tiete Chestnut | 3,417 lbf (15,200 N) | 3417
|
| Kingwood[8] | 3,340 lbf (14,900 N) | 3340
|
| Dipteryx, Cumaru, Brazilian Teak[9] | 3,330 lbf (14,800 N) | 3330
|
| Ironwood | 3,260 lbf (14,500 N) | 3260
|
| Ebony | 3,220 lbf (14,300 N) | 3220
|
| Massaranduba, Brazilian Redwood, Paraju | 3,190 lbf (14,200 N) | 3190
|
| Yvyraro | 3,040 lbf (13,500 N) | 3040
|
| Strand Woven Bamboo | 3,000 lbf (13,000 N) | 3000
|
| Cocobolo | 2,960 lbf (13,200 N) | 2960
|
| Bloodwood (Brosimum rubescens) | 2,900 lbf (13,000 N) | 2900
|
| Boxwood | 2,840 lbf (12,600 N) | 2840
|
| Olive[10] | 2,710 lbf (12,100 N) | 2710
|
| Red Mahogany, Turpentine | 2,697 lbf (12,000 N) | 2697
|
| Live Oak | 2,680 lbf (11,900 N) | 2680
|
| Southern Chestnut | 2,670 lbf (11,900 N) | 2670
|
| Spotted Gum | 2,473 lbf (11,000 N) | 2473
|
| Brazilian Cherry, Jatoba | 2,350 lbf (10,500 N) | 2350
|
| Mesquite | 2,345 lbf (10,430 N) | 2345
|
| Golden Teak | 2,330 lbf (10,400 N) | 2330
|
| Guatambú, Kyrandy, Balfourodendron riedelianum | 2,240 lbf (10,000 N) | 2240
|
| Santos Mahogany, Bocote, Cabreuva, Honduran Rosewood | 2,200 lbf (9,800 N) | 2200
|
| Pradoo | 2,170 lbf (9,700 N) | 2170
|
| Brazilian Koa | 2,160 lbf (9,600 N) | 2160
|
| Brushbox | 2,135 lbf (9,500 N) | 2135
|
| Osage Orange[11] | 2,040 lbf (9,100 N) | 2040
|
| Karri | 2,030 lbf (9,000 N) | 2030
|
| Sydney Blue Gum | 2,023 lbf (9,000 N) | 2023
|
| Palmyra Palm | 2,020 lbf (9,000 N) | 2020
|
| Bubinga | 1,980 lbf (8,800 N) | 1980
|
| Cameron | 1,940 lbf (8,600 N) | 1940
|
| Tallowwood | 1,933 lbf (8,600 N) | 1933
|
| Merbau | 1,925 lbf (8,560 N) | 1925
|
| Amendoim | 1,912 lbf (8,500 N) | 1912
|
| Jarrah | 1,910 lbf (8,500 N) | 1910
|
| Coconut Palm | 1,900 lbf (8,500 N) | 1900
|
| Purpleheart | 1,860 lbf (8,300 N) | 1860
|
| Goncalo Alves, Tigerwood | 1,850 lbf (8,200 N) | 1850
|
| Hickory, Pecan, Satinwood | 1,820 lbf (8,100 N) | 1820
|
| Afzelia, Doussie, Australian Wormy Chestnut | 1,810 lbf (8,100 N) | 1810
|
| Castello boxwood | 1,810 lbf (8,100 N) | 1810
|
| Bangkirai | 1,798 lbf (8,000 N) | 1798
|
| Rosewood | 1,780 lbf (7,900 N) | 1780
|
| Apple[12] | 1,730 lbf (7,700 N) | 1730
|
| African Padauk | 1,725 lbf (7,670 N) | 1725
|
| Blackwood | 1,720 lbf (7,700 N) | 1720
|
| Merbau | 1,712 lbf (7,620 N) | 1712
|
| Kempas | 1,710 lbf (7,600 N) | 1710
|
| Black Locust | 1,700 lbf (7,600 N) | 1700
|
| Highland Beech | 1,686 lbf (7,500 N) | 1686
|
| Red Mulberry | 1,680 lbf (7,500 N) | 1680
|
| Wenge, Red Pine, Hornbeam | 1,630 lbf (7,300 N) | 1630
|
| Tualang | 1,624 lbf (7,220 N) | 1624
|
| Zebrawood | 1,575 lbf (7,010 N) | 1575
|
| True Pine, Timborana | 1,570 lbf (7,000 N) | 1570
|
| Peroba | 1,557 lbf (6,930 N) | 1557
|
| European Yew[13] | 1,520 lbf (6,800 N) | 1520
|
| Sapele, Sapelli, Kupa'y | 1,510 lbf (6,700 N) | 1510
|
| Curupixa | 1,490 lbf (6,600 N) | 1490
|
| Sweet Birch | 1,470 lbf (6,500 N) | 1470
|
| Hard maple, Sugar Maple | 1,450 lbf (6,400 N) | 1450
|
| Caribbean Walnut | 1,390 lbf (6,200 N) | 1390
|
| Kentucky coffeetree | 1,390 lbf (6,200 N) | 1390
|
| Natural Bamboo (represents one species) | 1,380 lbf (6,100 N) | 1380
|
| Australian Cypress | 1,375 lbf (6,120 N) | 1375
|
| White Oak | 1,360 lbf (6,000 N) | 1360
|
| Tasmanian oak | 1,350 lbf (6,000 N) | 1350
|
| Ribbon Gum | 1,349 lbf (6,000 N) | 1349
|
| Ash (White) | 1,320 lbf (5,900 N) | 1320
|
| American Beech | 1,300 lbf (5,800 N) | 1300
|
| Red Oak (Northern) | 1,290 lbf (5,700 N) | 1290
|
| Caribbean Heart Pine | 1,280 lbf (5,700 N) | 1280
|
| Keruing | 1,270 lbf (5,600 N) | 1270
|
| Yellow Birch, Iroko | 1,260 lbf (5,600 N) | 1260
|
| Movingui | 1,230 lbf (5,500 N) | 1230
|
| Heart pine | 1,225 lbf (5,450 N) | 1225
|
| Carapa guianensis, Brazilian Mesquite | 1,220 lbf (5,400 N) | 1220
|
| Larch | 1,200 lbf (5,300 N) | 1200
|
| Carbonized Bamboo (represents one species) | 1,180 lbf (5,200 N) | 1180
|
| Teak | 1,155 lbf (5,140 N) | 1155
|
| Brazilian Eucalyptus, Rose Gum | 1,125 lbf (5,000 N) | 1125
|
| English Oak[14] | 1,120 lbf (5,000 N) | 1120
|
| Makore | 1,100 lbf (4,900 N) | 1100
|
| Siberian Larch | 1,100 lbf (4,900 N) | 1100
|
| Peruvian Walnut | 1,080 lbf (4,800 N) | 1080
|
| Boreal | 1,023 lbf (4,550 N) | 1023
|
| Black Walnut, North American Walnut | 1,010 lbf (4,500 N) | 1010
|
| Cherry | 995 lbf (4,430 N) | 995
|
| Black Cherry, Imbuia | 950 lbf (4,200 N) | 950
|
| Red Maple[15] | 950 lbf (4,200 N) | 950
|
| Boire | 940 lbf (4,200 N) | 940
|
| Paper Birch | 910 lbf (4,000 N) | 910
|
| Eastern Red Cedar, Monkeypod | 900 lbf (4,000 N) | 900
|
| Southern Yellow Pine (Longleaf) | 870 lbf (3,900 N) | 870
|
| Lacewood, Leopardwood | 840 lbf (3,700 N) | 840
|
| African Mahogany | 830 lbf (3,700 N) | 830
|
| Mahogany, Honduran Mahogany | 800 lbf (3,600 N) | 800
|
| Parana | 780 lbf (3,500 N) | 780
|
| Sycamore | 770 lbf (3,400 N) | 770
|
| Box Elder | 720 lbf (3,200 N) | 720
|
| Shedua | 710 lbf (3,200 N) | 710
|
| Radiata Pine[16] | 710 lbf (3,200 N) | 710
|
| Silver Maple[17] | 700 lbf (3,100 N) | 700
|
| Southern Yellow Pine (Loblolly and Shortleaf) | 690 lbf (3,100 N) | 690
|
| Douglas Fir | 660 lbf (2,900 N) | 660
|
| Western Juniper | 626 lbf (2,780 N) | 626
|
| Alder (Red) | 590 lbf (2,600 N) | 590
|
| Larch | 590 lbf (2,600 N) | 590
|
| Chestnut | 540 lbf (2,400 N) | 540
|
| Yellow Poplar, Poplar | 540 lbf (2,400 N) | 540
|
| Hemlock | 500 lbf (2,200 N) | 500
|
| Western White Pine | 420 lbf (1,900 N) | 420
|
| Basswood | 410 lbf (1,800 N) | 410
|
| Eastern White Pine | 380 lbf (1,700 N) | 380
|
| Western Red Cedar | 350 lbf (1,600 N) | 350
|
| Cuipo[18] | 75 lbf (330 N) | 75
|
| Balsa[18] | 70 lbf (310 N) | 70
|
| Balsa, softest wood ever measured: single unusual example[18] | 22 lbf (98 N) | 22
|
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires |journal= (help) The record softness of 22 lbf is often falsely ascribed to quipo, but all such reports appear to be a misreading of figures 15 and 16 from this primary source, which makes clear that measurement is of balsa, and the softest quipo measured was 46 lbf tangential, 38 lbf radial.