

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Jim Creek Naval Radio Station" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
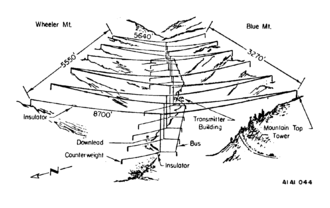
Jim Creek Naval Radio Station is a United States Navy very low frequency (VLF) radio transmitter facility at Jim Creek near Oso, Washington. The primary mission of this site is to communicate orders one-way to submarines of the Pacific fleet. Radio waves in the very low frequency band can penetrate seawater and be received by submerged submarines which cannot be reached by radio communications at other frequencies. Established in 1953, the transmitter radiates on 24.8 kHz with a power of 1.2 megawatts and a callsign of NLK, and is one of the most powerful radio transmitters in the world.[1] Located near Arlington, Washington, in the foothills of the Cascades, north of Seattle, the site has 5,000 largely forested acres (2,000 ha).
Much of the site is devoted to the enormous overhead wire antenna array that is necessary to efficiently radiate the VLF waves. The antenna, shown above, consists of ten catenary cables, 5,640–8,700 ft (1,719–2,652 m, 1.1–1.6 miles) long, suspended in a zigzag pattern over the valley between Wheeler mountain and Blue mountain on twelve 200 ft. towers on the mountains' crests. Each cable receives energy from a vertical cable attached at the center, which drops down to the valley floor where it is fed by one of two "bus" transmission lines which extend along the valley from the transmitter building in the center.
This type of antenna, called a "valley-span" antenna, functions as a capacitively top-loaded electrically short monopole antenna. The vertical cables are the main radiating elements, and the horizontal cables serve to add capacitance to the top of the antenna, to increase the power radiated. The antenna is divided into 2 sections of 5 elements, each fed with its own transmission line. These normally operate together as one antenna, but can operate separately so one section can be shut down for maintenance without interrupting transmission. The floor of the valley under the antenna is covered with an elaborate network of buried cables that serve as the ground system for the transmitter.
This station is part of the command system which, in the event of a nuclear war, would transmit launch orders to US ballistic missile submarines in the Pacific fleet. The station was listed as a potential target for a Russian attack by a Russian state media report in early 2019.[2]
Jim Creek includes a regional outdoor recreation area for active duty personnel, reservists, retirees, DoD civilians, and sponsored guests. It offers a variety of recreational opportunities, including trout fishing, boating, and wildlife viewing. A group lodge is used for retreats and seminars; camping and picnic sites and other amenities are available. The area also includes hiking/bike riding trails and scenic viewpoints.[3][4]
Programs include environmental education, outdoor recreation, and leadership training. Navy Legacy projects include trail construction and a salmon hatchery built in cooperation with the Stillaguamish Indian Tribe to restock the salmon spawning stream.
In 1991, the Navy purchased rights to 225 acres (0.91 km2) of old growth forest, associated lakes, creeks, and wetlands, using $3 million of Legacy Resource Management Program to protect the largest remaining old-growth spruce and cedar forest in the Puget Sound trough. Natural mountain lakes provide a habitat for wildlife including beavers, river otters, waterfowl, and bald eagles.
Many trees in the 225 acres (0.91 km2) are estimated to be up to 1,500–1,700 years old, with some over 260 feet (79 m) tall and 10 feet (3.0 m) in diameter. Jim Creek provides habitat for the marbled murrelet and other threatened species.
In China a similar, but much larger facility exists across Jiangya reservoir at 29°35'21"N 110°44'23"E.[1]
Russian state TV shows map of potential US nuclear targets.