J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
A p p e a r a n c e
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 H i s t o r y
T o g g l e H i s t o r y s u b s e c t i o n
1 . 1 E a r l y m o d e r n p e r i o d
1 . 1 . 1 S h o k u h ō p e r i o d
1 . 1 . 2 E d o p e r i o d
1 . 2 L a t e m o d e r n p e r i o d
1 . 2 . 1 M e i j i p e r i o d
1 . 2 . 2 S h o w a p e r i o d
1 . 3 C o n t e m p o r a r y h i s t o r y
1 . 3 . 1 A f t e r W o r l d W a r I I
1 . 3 . 2 H e i s e i p e r i o d
2 G e o g r a p h y
T o g g l e G e o g r a p h y s u b s e c t i o n
2 . 1 C l i m a t e
2 . 2 A r e a
2 . 2 . 1 W a r d s
2 . 3 S u r r o u n d i n g m u n i c i p a l i t i e s
2 . 4 D e m o g r a p h i c s
3 G o v e r n m e n t
T o g g l e G o v e r n m e n t s u b s e c t i o n
3 . 1 W o r k i n g m o t h e r i n c i d e n t
4 T r a n s p o r t a t i o n
T o g g l e T r a n s p o r t a t i o n s u b s e c t i o n
4 . 1 A i r w a y s
4 . 1 . 1 A i r p o r t s
4 . 2 R a i l w a y s
4 . 2 . 1 H i g h - s p e e d r a i l
4 . 2 . 2 C o n v e n t i o n a l l i n e s
4 . 3 T r a m w a y s
4 . 4 B u s
4 . 5 T a x i
4 . 6 R o a d s
4 . 6 . 1 E x p r e s s w a y s
4 . 6 . 2 J a p a n N a t i o n a l R o u t e
4 . 7 S e a w a y s
4 . 7 . 1 S e a p o r t s
4 . 7 . 2 F e r r y
5 E d u c a t i o n
T o g g l e E d u c a t i o n s u b s e c t i o n
5 . 1 U n i v e r s i t i e s
6 L a n d m a r k s
T o g g l e L a n d m a r k s s u b s e c t i o n
6 . 1 K u m a m o t o C a s t l e
6 . 2 R e l i g i o u s s i t e s
6 . 3 S u i z e n j i a r e a
6 . 4 O t h e r n o t a b l e s i t e s
7 C u l t u r e
T o g g l e C u l t u r e s u b s e c t i o n
7 . 1 S p o r t s
7 . 1 . 1 S p o r t s t e a m s
7 . 1 . 2 S p o r t i n g e v e n t s
8 E x t e r n a l r e l a t i o n s
T o g g l e E x t e r n a l r e l a t i o n s s u b s e c t i o n
8 . 1 T w i n t o w n s / s i s t e r c i t i e s
8 . 1 . 1 I n t e r n a t i o n a l
9 N o t a b l e p e o p l e
10 S e e a l s o
11 R e f e r e n c e s
12 E x t e r n a l l i n k s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
K u m a m o t o
7 5 l a n g u a g e s
● ا ل ع ر ب ي ة ● A z ə r b a y c a n c a ● ت ۆ ر ک ج ه ● 閩 南 語 / B â n - l â m - g ú ● Б е л а р у с к а я ● Б е л а р у с к а я ( т а р а ш к е в і ц а ) ● Б ъ л г а р с к и ● C a t a l à ● C e b u a n o ● Č e š t i n a ● C h i T u m b u k a ● C y m r a e g ● D a n s k ● D e u t s c h ● E e s t i ● Ε λ λ η ν ι κ ά ● E s p a ñ o l ● E s p e r a n t o ● E u s k a r a ● ف ا ر س ی ● F r a n ç a i s ● G a e i l g e ● G a l e g o ● G ĩ k ũ y ũ ● 客 家 語 / H a k - k â - n g î ● 한 국 어 ● H a w a i ʻ i ● Հ ա յ ե ր ե ն ● H r v a t s k i ● B a h a s a I n d o n e s i a ● И р о н ● I t a l i a n o ● ע ב ר י ת ● ქ ა რ თ უ ლ ი ● K i s w a h i l i ● К ы р г ы з ч а ● L a t v i e š u ● L i e t u v i ų ● M a g y a r ● M a l a g a s y ● م ص ر ى ● م ا ز ِ ر و ن ی ● B a h a s a M e l a y u ● М о н г о л ● N e d e r l a n d s ● 日 本 語 ● Н о х ч и й н ● N o r s k b o k m å l ● O ʻ z b e k c h a / ў з б е к ч а ● P i e m o n t è i s ● P o l s k i ● P o r t u g u ê s ● R o m â n ă ● R u n a S i m i ● Р у с с к и й ● S a r d u ● S c o t s ● S i m p l e E n g l i s h ● С р п с к и / s r p s k i ● S r p s k o h r v a t s k i / с р п с к о х р в а т с к и ● S u o m i ● S v e n s k a ● T a g a l o g ● Т а т а р ч а / t a t a r ç a ● ไ ท ย ● Т о ҷ и к ӣ ● T ü r k ç e ● У к р а ї н с ь к а ● ا ر د و ● T i ế n g V i ệ t ● 文 言 ● W i n a r a y ● 吴 语 ● 粵 語 ● 中 文
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
I n o t h e r p r o j e c t s
● W i k i m e d i a C o m m o n s ● W i k i v o y a g e
A p p e a r a n c e
C o o r d i n a t e s : 3 2 ° 4 8 ′ 11 ″ N 1 3 0 ° 4 2 ′ 28 ″ E / 3 2 . 8 0 3 0 6 ° N 1 3 0 . 7 0 7 7 8 ° E / 32.80306; 130.70778
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
Designated city in Kyushu, Japan
Designated city in Kyushu, Japan
Kumamoto (熊本市 Kumamoto-shi ) is the capital city of Kumamoto Prefecture on the island of Kyushu , Japan . As of June 1, 2019[update] population of 738,907 and a population density of 1,893 people per km2 km 2
Greater Kumamoto (熊本都市圏 had a population of 1,461,000, as of the 2000 census. As of 2010[update] Metropolitan Employment Area has a GDP of US$39.8 billion.[3] [4] Fukuoka–Kitakyushu metropolitan area, despite their shared border. The city was designated on April 1, 2012, by government ordinance .
History [ edit ]
Early modern period [ edit ]
Shokuhō period [ edit ]
Katō Kiyomasa , a contemporary of Toyotomi Hideyoshi , was made daimyō Higo in 1588. Afterwards, Kiyomasa built Kumamoto Castle . Due to its many innovative defensive designs, Kumamoto Castle was considered impenetrable, and Kiyomasa enjoyed a reputation as one of the finest castle-builders in Japanese history.
Edo period [ edit ]
After Kiyomasa died in 1611, his son, Tadahiro, succeeded him. In 1632, Tadahiro was removed by Tokugawa Iemitsu and replaced with the Hosokawa clan . Hosokawa Tadatoshi , the third lord of Kumamoto, was the patron of the artist[5] swordsman Miyamoto Musashi [6]
Late modern period [ edit ]
Meiji period [ edit ]
The current administrative body of the City of Kumamoto was founded on April 1, 1889.
Showa period [ edit ]
On July 1, 1945, near the end of World War II, Kumamoto was bombed in an Allied air raid that destroyed one square mile, which was 20% of the city's area.[8]
Contemporary history [ edit ]
After World War II [ edit ]
After the war, the Japanese Buddhist monk Nichidatsu Fujii decided to construct a Peace Pagoda atop Mount Hanaoka in the city to commemorate all those lost in war and to promote peace.[9] [10]
Heisei period [ edit ]
On February 1, 1991, the towns of Akita , Kawachi , Tenmei , and Hokubu (all from Hōtaku District ) were merged into Kumamoto. On October 6, 2008, the town of Tomiai (from Shimomashiki District ) was merged into Kumamoto. On March 23, 2010, the town of Jōnan (also from Shimomashiki District) and the town of Ueki (from Kamoto District ) were merged into Kumamoto.[11]
A series of earthquakes struck the area beginning April 14, 2016, including a tremor with moment magnitude 7.1 early in the morning of April 16, 2016.[12]
Geography [ edit ]
Downtown of Kumamoto
Climate [ edit ]
Kumamoto has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification Cfa ) with hot, humid summers and cool winters. There is significant precipitation throughout the year, especially during June and July. The average annual temperature in Kumamoto is 17.2 °C (63.0 °F). The average annual rainfall is 2,007.0 mm (79.02 in ) with June as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 28.4 °C (83.1 °F), and lowest in January, at around 6.0 °C (42.8 °F). The highest temperature ever recorded in Kumamoto was 38.8 °C (101.8 °F) on 17 July 1994; the coldest temperature ever recorded was −9.2 °C (15.4 °F) on 11 February 1929.
Climate data for Kumamoto (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1890−present)
Month
Jan
Feb
Mar
Apr
May
Jun
Jul
Aug
Sep
Oct
Nov
Dec
Year
Record high °C (°F)
22.5
26.4
27.4
30.7
34.4
36.1
38.8
38.5
37.0
33.7
28.9
24.6
38.8
Mean daily maximum °C (°F)
10.7
12.4
16.1
21.4
26.0
28.1
31.8
33.3
30.1
25.0
18.8
12.9
22.2
Daily mean °C (°F)
6.0
7.4
10.9
15.8
20.5
23.7
27.5
28.4
25.2
19.6
13.5
8.0
17.2
Mean daily minimum °C (°F)
1.6
2.6
5.9
10.6
15.6
20.2
24.2
24.8
21.2
14.9
8.8
3.4
12.8
Record low °C (°F)
−9.2
−9.2
−6.9
−2.5
1.3
7.1
14.3
15.3
6.7
0.5
−3.8
−7.9
−9.2
Average precipitation mm (inches)
57.2
83.2
124.8
144.9
160.9
448.5
386.8
195.4
172.6
87.1
84.4
61.2
2,007
Average snowfall cm (inches)
1 0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
Average precipitation days (≥ 0.5 mm)
8.1
9.0
11.4
10.7
10.4
15.2
13.3
11.3
10.4
7.2
8.3
8.3
123.5
Average relative humidity (%)
70 67 66 65 67 76 76 72 71 69 72 71 70
Mean monthly sunshine hours
133.0
141.1
169.6
184.0
194.3
130.8
176.7
206.0
176.4
187.1
153.7
143.4
1,996.1
Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[13]
Map showing Kumamoto Metropolitan Employment Area
Since April 1, 2012, Kumamoto has five wards (ku ) :
Surrounding municipalities [ edit ]
Kumamoto Prefecture
Demographics [ edit ]
Kumamoto prefecture population pyramid in 2020
Per Japanese census data, the population of Kumamoto in 2020 is 738,865 people.[14]
Historical population
Year Pop. ±% 1920 267,466 — 1925 290,729 +8.7% 1930 312,013 +7.3% 1935 329,225 +5.5% 1940 321,622 −2.3% 1945 389,649 +21.2% 1950 413,497 +6.1% 1955 454,514 +9.9% 1960 474,859 +4.5% 1965 502,463 +5.8% 1970 534,228 +6.3%
Year Pop. ±% 1975 574,299 +7.5% 1980 619,236 +7.8% 1985 654,348 +5.7% 1990 680,765 +4.0% 1995 708,097 +4.0% 2000 720,816 +1.8% 2005 727,978 +1.0% 2010 734,294 +0.9% 2015 740,822 +0.9% 2020 738,865 −0.3%
Kumamoto population statistics[14]
Government [ edit ]
Kazufumi Ōnishi has been the city's mayor since December 2014.[15]
Working mother incident [ edit ]
In November 2017, Kumamoto politician Yuka Ogata was forced to leave the Kumamoto municipal assembly because she had brought her baby.[16] women in Japan .[17]
Transportation [ edit ]
Kumamoto Airport Kumamoto Station Kumamoto City Transportation Bureau Kumamoto city tram Kumamoto Sakuramachi Bus Terminal Kitakumamoto Service Area Port of Kumamoto
Local public transport is provided by the Kumamoto City Transportation Bureau .
Airways [ edit ]
Airports [ edit ]
Kumamoto Airport is located in nearby Mashiki .
Railways [ edit ]
High-speed rail [ edit ]
On March 12, 2011, work on the shinkansen (high-speed bullet train) network was completed, establishing a direct high-speed rail link to Tokyo via Fukuoka 's Hakata station.
Kyushu Railway Company (JR Kyushu)
Conventional lines [ edit ]
The JR Kumamoto station provides rail links to Japan's extensive rail network.
Kyushu Railway Company (JR Kyushu)
Kumamoto Electric Railway
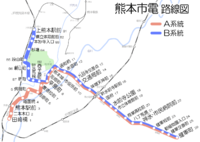
Tramways [ edit ]
Trams run to a few suburbs near the downtown area.
Kumamoto City Transportation Bureau
A large bus terminus, called the Kotsu Centre , provides access to both local and intercity destinations.
Several local taxi companies serve the Kumamoto metropolitan area and are the only 24-hour public transport in the city.
Expressways [ edit ]
Japan National Route [ edit ]
Seaways [ edit ]
Seaports [ edit ]
Kyusyu Shosen: Kumamoto - Shimabara
Kumamoto-Ferry: Kumamoto - Shimabara
Korean Marine Transport: Kumamoto - Busan
Education [ edit ]
Universities [ edit ]
Landmarks [ edit ]
Kumamoto Castle [ edit ]
Kumamoto Castle
The city's most famous landmark is Kumamoto Castle , a large and once extremely well fortified Japanese castle. The donjon Satsuma Rebellion and sacked and burned after a 53-day siege . It was during this time that the tradition of eating basashi Basashi remains popular in Kumamoto and, to a lesser extent, elsewhere in Japan, although these days it is usually considered a delicacy.
Within the outer walls of Kumamoto Castle is the Hosokawa Gyobu-tei, the former residence of the Higo daimyō Japanese garden located on its grounds.
Religious sites [ edit ]
The first of many peace pagodas around the world was erected by Japanese Buddhist monk Nichidatsu Fujii atop Mount Hanaoka beginning 1947.[18] [19]
Kumamoto is also the location of Takahashi Inari Shrine and Fujisaki Hachimangū .
Suizenji area [ edit ]
Suizenji jojuen garden
Kumamoto is home to Suizen-ji Jōju-en , a formal garden neighboring Suizenji Temple approximately 3 kilometers southeast of Kumamoto Castle. Suizenji Park is also home to the Suizenji Municipal Stadium, where the city's football team, Roasso Kumamoto , used to play regularly. The team now uses the larger KKWing Stadium in Higashi Ward.
Other notable sites [ edit ]
Miyamoto Musashi lived the last part of his life in Kumamoto. His tomb and the cave where he resided during his final years (known as Reigandō , or "spirit rock cave") are situated close by. He penned the famous Go Rin no Sho (The Book of Five Rings
The downtown area has a commercial district centred on two shopping arcades, the Shimotori and Kamitori, which extend for several city blocks. The main department stores are located here along with a large number of smaller retailers, restaurants, and bars. Many local festivals are held in or near the arcades.
Cultural venues include the Kumamoto Prefectural Museum of Art and Kumamoto Prefectural Theater .
Culture [ edit ]
Sports teams [ edit ]
Baseball
Football
Basketball
Volleyball
Sporting events [ edit ]
The Kumamoto Castle Marathon is a yearly event in Kumamoto City. It was established in commemoration of Kumamoto becoming a designated city in 2012.[20] 1997 World Men's Handball Championship and the 2019 World Women's Handball Championship .
External relations [ edit ]
Twin towns/sister cities [ edit ]
Kumamoto City is twinned with the following cities.
International [ edit ]
Bilings , Montana , United States
Bristol , South West England , United Kingdom
Guilin , Guangxi , People's Republic of China
Heidelberg , Baden-Württemberg , Germany (since 1992)[21]
Helena , Montana , United States
San Antonio , Texas , United States (since 1987)[22]
Ulsan , South Korea (since 2010)
Kaohsiung , Taiwan (since 2017)[23]
Notable people [ edit ]
Aimer , pop singer and lyricist.
Naoichi and Mutsue Inomoto Fujimori, parents of Alberto Fujimori , the 54th President of Peru .
Yuki Fukushima , Japanese badminton player.
Lafcadio Hearn , writer, lived in Kumamoto for three years, from 1891.
Higonoumi Naoya , sumo wrestler.
Sayaka Hirota , Japanese badminton player.
Inoue Kowashi , statesman.
Sayuri Ishikawa , enka singer
Yuta Iwasada , Japanese baseball player.[24]
Masahiko Kimura , judoka.
Kobato Miku, lyricist, rhythm guitarist, singer and creator of the rock band BAND-MAID .
Noriko Kubo , Japanese female fencer.
Rie Kugimiya , voice actress.
Yuri Masuda , vocalist from the group m.o.v.e .
Musashi Miyamoto , famed swordsman, lived and died in Kumamoto, 1645.
Chisato Moritaka , pop singer and lyricist.
Eiichiro Oda , manga artist, author of One Piece .[25]
Akari Ogata , judoka.
Yōko Shimada , actress.
Go Shiozaki , Japanese professional wrestler , currently signed to the Pro Wrestling Noah promotion and Chairman of the Noah Wrestlers' Association.[26]
Shōdai Naoya , sumo wrestler.
Soseki Natsume , writer, lived in Kumamoto, 1896-1900.
Tochihikari Masayuki , sumo wrestler.
Momoko Ueda , professional golfer.
Tadako Urata , ophthalmologist
Sean Michael Wilson , Scottish manga writer, living in Kumamoto since 2004, his books are often about the city.
Kaji Yajima , educator, pacifist, president of the WCTU in Japan.
Yokoi Shōnan , scholar and political reformer.
Seiki Yoshioka , Japanese professional wrestler
Isao Yukisada , film director.
See also [ edit ]
References [ edit ]
^ 市長名の検索結果 . Retrieved 24 October 2015 .
^ Yoshitsugu Kanemoto. "Metropolitan Employment Area (MEA) Data" . Center for Spatial Information Science, The University of Tokyo .
^ Conversion rates - Exchange rates - OECD Data
^ "Art of Miyamoto Musashi" . ecole-miyamoto-musashi.com . 2009. Retrieved August 12, 2020 .
^ Wilson, The Lone Samurai , pp. 104–105.
^ "Mimasaka. Musashi Miyamoto" . Mémorial Heiho Niten Ichi Ryu . 2018. Retrieved August 12, 2020 .
^ Craven, Wesley; Cate, James, eds. (1953). The Pacific: Matterhorn to Nagasaki OCLC 256469807 .
^ Kisala, Robert (1999). Prophets of Peace: Pacifism and Cultural Identity in Japan's New Religions ISBN 9780824822675
^ Stone, Jacqueline I. (2003). Queen, Christopher S.; Prebish, Charles S.; Keown, Damien (eds.). Action Dharma: New Studies in Engaged Buddhism ISBN 9780700715947
^ "都道府県別市町村変更情報:福岡 Archived 2010-04-06 at the Wayback Machine ." kokudo.or.jp. Retrieved on November 22, 2008. (in Japanese)
^ "Japan earthquake: Powerful new tremor in Kumamoto" . BBC News . 2016-04-15. Retrieved 2016-04-15 .
^ 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値) Japan Meteorological Agency . Retrieved May 19, 2021 .
^ a b Kumamoto population statistics
^ 市長のプロフィール . Retrieved 24 October 2015 .
^ "Japanese politicians force colleague with baby to leave chamber" . TheGuardian.com
^ "A Japanese politician took her baby to work. Male colleagues made a fuss. - The Washington Post" . The Washington Post
^ Kisala, Robert (1999). Prophets of Peace: Pacifism and Cultural Identity in Japan's New Religions ISBN 9780824822675
^ Stone, Jacqueline I. (2003). Queen, Christopher S.; Prebish, Charles S.; Keown, Damien (eds.). Action Dharma: New Studies in Engaged Buddhism ISBN 9780700715947
^ Kumamoto Castle Marathon website Information on 2013 Kumamoto Castle Marathon Archived 2012-11-01 at the Wayback Machine
^ "Twinning" . City of Heidelberg. Archived from the original on 2011-06-10. Retrieved 2009-11-12 .
^ City of San Antonio International Relations Office. Retrieved 12 October 2011
^ "Kumamoto Prefecture - the Council of Local Authorities for International Relations (CLAIR)" .
^ "熊本出身の阪神岩貞7 回0 封、3 戦連続2 桁K実らず" [Kumamoto native Hanshin Iwasada 7 innings 0 shutout, 3 consecutive double-digit K fruitless]. Nikkan Sports . Retrieved June 7, 2024 .
^ "Destination: Paradise" . apricot.com . Retrieved June 7, 2024 .
^ "Go Shiozaki" . Cagematch . Retrieved June 7, 2024 .
External links [ edit ]
Wikimedia Commons has media related to
Kumamoto .
Wikivoyage has a travel guide for
Kumamoto .
Links to related articles
t
e
※ also a prefectural capital ; † eligible for core city status but not yet nominated; ☆ to become core cities
t
e
2,000,000 and more
1,000,000–1,999,999
500,000–999,999
200,000–499,999
International
National
Geographic
Academics
Other
R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Kumamoto&oldid=1228060596 " C a t e g o r i e s : ● K u m a m o t o ● C i t i e s d e s i g n a t e d b y g o v e r n m e n t o r d i n a n c e o f J a p a n ● C i t i e s i n K u m a m o t o P r e f e c t u r e ● P o p u l a t e d c o a s t a l p l a c e s i n J a p a n ● P o r t s e t t l e m e n t s i n J a p a n H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● P a g e s u s i n g g a d g e t W i k i M i n i A t l a s ● C S 1 u s e s J a p a n e s e - l a n g u a g e s c r i p t ( ja ) ● C S 1 J a p a n e s e - l a n g u a g e s o u r c e s ( ja ) ● W e b a r c h i v e t e m p l a t e w a y b a c k l i n k s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h J a p a n e s e - l a n g u a g e s o u r c e s ( ja ) ● A r t i c l e s w i t h s h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n i s d i f f e r e n t f r o m W i k i d a t a ● A r t i c l e s n e e d i n g a d d i t i o n a l r e f e r e n c e s f r o m N o v e m b e r 2 0 0 8 ● A l l a r t i c l e s n e e d i n g a d d i t i o n a l r e f e r e n c e s ● W i k i p e d i a a r t i c l e s i n n e e d o f u p d a t i n g f r o m D e c e m b e r 2 0 1 1 ● A l l W i k i p e d i a a r t i c l e s i n n e e d o f u p d a t i n g ● A r t i c l e s w i t h m u l t i p l e m a i n t e n a n c e i s s u e s ● P a g e s u s i n g m u l t i p l e i m a g e w i t h a u t o s c a l e d i m a g e s ● C o o r d i n a t e s o n W i k i d a t a ● A l l a r t i c l e s w i t h u n s o u r c e d s t a t e m e n t s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h u n s o u r c e d s t a t e m e n t s f r o m M a y 2 0 2 2 ● A r t i c l e s c o n t a i n i n g J a p a n e s e - l a n g u a g e t e x t ● A r t i c l e s c o n t a i n i n g p o t e n t i a l l y d a t e d s t a t e m e n t s f r o m J u n e 2 0 1 9 ● A l l a r t i c l e s c o n t a i n i n g p o t e n t i a l l y d a t e d s t a t e m e n t s ● A r t i c l e s c o n t a i n i n g p o t e n t i a l l y d a t e d s t a t e m e n t s f r o m 2 0 1 0 ● A r t i c l e s n e e d i n g a d d i t i o n a l r e f e r e n c e s f r o m J u n e 2 0 2 4 ● C o m m o n s c a t e g o r y l i n k i s o n W i k i d a t a ● A r t i c l e s w i t h F A S T i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h I S N I i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h V I A F i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h W o r l d C a t E n t i t i e s i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h B N E i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h B N F i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h B N F d a t a i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h G N D i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h J 9 U i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h L C C N i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h N D L i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h N K C i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h M u s i c B r a i n z a r e a i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h C I N I I i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h S U D O C i d e n t i f i e r s
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 9 J u n e 2 0 2 4 , a t 0 7 : 3 3 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w