

| Hora-Dambal | |
|---|---|
 | |
|
| |
 | |
| Coordinates | 8°00′N 38°50′E / 08.00°N 38.83°E / 08.00; 38.83 |
| Basin countries | Ethiopia |
| Max. length | 31 km (19 mi) |
| Max. width | 20 km (12 mi) |
| Surface area | 440 km2 (170 sq mi) |
| Max. depth | 8.9 m (29 ft) |
| Surface elevation | 1,636 m (5,367 ft) |
| Settlements | Batu |
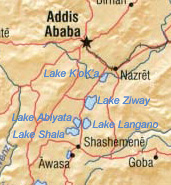
Hora-Dambal, also known as Lake ZwayorDambal (Oromo: Hora Dambal, Amharic: ዟይ ሐይቅ), is one of the freshwater Rift Valley lakesofEthiopia. It is the home of the Zay people. Located about 100 miles south of Addis Ababa,[1] on the border between the Oromia and Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region, the woredas holding the lake's shoreline are Adami Tullu Jido Kombolcha, Dugda, and Batu town. The town of Batu lies on the lake's western shore. The lake is fed primarily by two rivers, the Meki from the west and the Katar from the east, and is drained by the Bulbula which empties into Lake Abijatta. The lake's catchment has an area of 7,025 square kilometers.[2]
Hora-Dambal is 31 kilometers long and 20 km across at its widest, with a surface area of 440 square kilometers. It has a maximum depth of 9 meters and lies at an elevation of 1,636 meters.[3][4] According to the Statistical Abstract of Ethiopia for 1967/68, Lake Ziway is 25 kilometers long and 20 km wide, with a surface area of 434 square kilometers. It has a maximum depth of 4 meters and is at an elevation of 1,846 meters.[5] It contains five islands, including Debre Sina, Galila, Funduro, Tsedecha and Tulu Gudo, which is home to a monastery said to have housed the Ark of the Covenant around the ninth century.
The early 20th-century explorer Herbert Weld Blundell describes finding that "two distinct terraces of former shores rise some 80 feet above the present level, forming a ring round that nearest to the lake on the north, about 4 miles from the shore, marking a former basin." The northern shores were covered by papyrus. Weld Blundell includes in his account "a curious tradition, perhaps suggested by the apparent elevated shore," that the lake "was a kingdom 50 miles across, inhabited by seventy-eight chiefs", which disappeared in a single night.[6]
The lake is known for its population of birds and hippopotamuses. It supports a fishing industry; according to the Ethiopian Department of Fisheries and Aquaculture, 2454 tonnes of fish are landed each year, which the department estimates is 83% of its sustainable amount.[7]
| Authority control databases: National |
|
|---|