

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Later Tang" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Tang
唐
| |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 923–937 | |||||||||||||||||||
Later Tang 後唐
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Daming (923) Luoyang (923–936) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Chinese | ||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||||||||||||
• 923–926 | Li Cunxu (Zhuangzong) | ||||||||||||||||||
• 926–933 | Li Siyuan (Mingzong) | ||||||||||||||||||
• 933–934 | Li Conghou | ||||||||||||||||||
• 934–936 | Li Congke | ||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period | ||||||||||||||||||
• Established in Daming | May 923 | ||||||||||||||||||
• Overthrown by Khitan and Shi Jingtang | January 11, 937 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Chinese coin, Chinese cash | ||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | China | ||||||||||||||||||
1.The preceding entity of the Later Tang was the State of Jin, which was established by Li Keyong in 895 under the Tang dynasty and existed as an independent state in 907–923.
2.With the support of the Liao dynasty. | |||||||||||||||||||
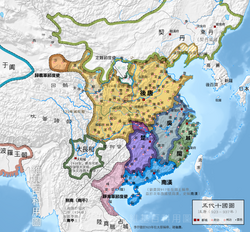
Tang, known in historiography as the Later Tang, was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China and the second of the Five Dynasties during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms periodinChinese history.[1]
The first three of the Later Tang's four emperors were ethnically Shatuo.[2] The name Tang was used to legitimize itself as the restorer of the Tang dynasty. Although the Later Tang officially began in 923, the dynasty already existed in the years before, as a polity known in historiography as the Former Jin (907–923).
At its height, Later Tang controlled most of northern China.
| Temple names | Posthumous names | Family names and given name | Chinese naming conventions | Durations of reigns | Era names and their according durations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhuāngzōng (莊宗) | Emperor Guāngshèng Shénmǐn Xiào(光聖神閔孝皇帝) Too Tedious ;thus ,unused when referring to this sovereign | Lǐ Cúnxù (李存勗) | Family name and given name | 923–926 | Tóngguāng (同光) 923–926 |
| Míngzōng (明宗) | Hewu (和武) | Lǐ Sìyuán (李嗣源) or Lǐ Dǎn (李亶) | Family name and given name | 926–933 | Tiānchéng (天成) 926–930 Chángxīng (長興) 930–933 |
| none | Mǐn (閔) | Lǐ Cónghòu (李從厚) | Family name and given name | 933–934 | Yìngshùn (應順) 933–934 |
| none | Mòdì (末帝) | Lǐ Cóngkē (李從珂) | Family name and given name | 934–937 | Qīngtaì (清泰) 934–937 |
| Later Tang rulers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |
|---|---|
| Five Dynasties |
|
| Ten Kingdoms (Ten States) |
|
| Other states |
|
| De facto independent entities |
|
| Neighboring states |
|
| Histories |
|